We curate the scientific literature to provide: Gene Ontology annotations to the GO Consortium and protein interaction data to the IMEx Consortium, this process is known as 'manual curation'.
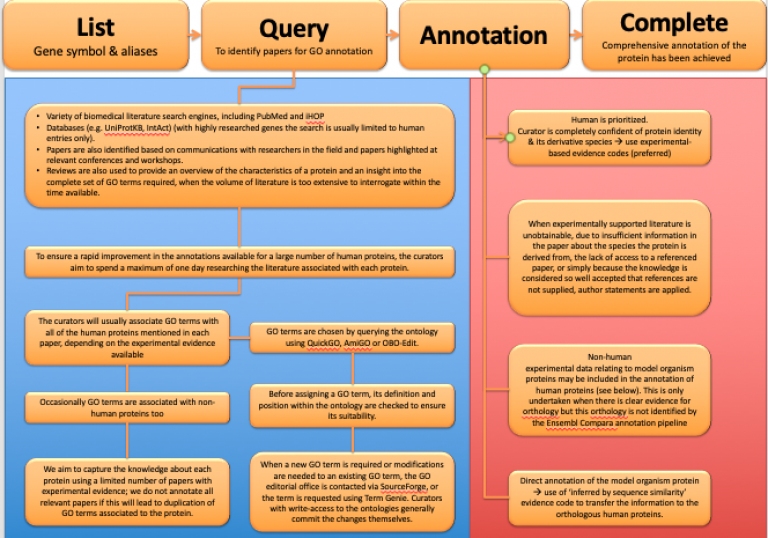
Manual gene annotation (biocuration) involves the extraction of information from published scientific papers (Balakrishnan et al., 2013, Orchard et al., 2014 & Huntley et al., 2015). In the resources we contribute to the majority of Gene Ontology (GO) or protein or molecular interaction annotations are attributed to an identified reference by use of a publication identifier and each annotation must indicate what kind of evidence supports the association between the gene product and the GO term, or the molecular/protein interaction. In addition, we are also creating new GO terms to enable the full description of the molecular function of gene product, its biological role in the cell and its cellular location.
The large-scale assignment of GO terms to human gene products using computational methods is a fast and efficient way of associating high-level terms to a large number of genes. However, to provide more reliable and specific annotations, GO curators use information from the published scientific literature to 'manually' associate highly descriptive GO terms to gene products. Similarly, protein interaction data is 'manually' captured from both high-throughput datasets, such as yeast-2-hybrid experiments as well as from small scale experimental data.
Consequently complete, highly detailed annotation of the processes and networks that a single gene product is involved in, may take a considerable time, depending on the number of published papers describing the gene product, and the complexity of the papers being annotated. These gene product annotations enable researchers to rapidly evaluate and interpret data and generate hypotheses to guide future research into cardiovascular and neurological processes.
In addition, as active members of the GO Consortium we participate in discussions about guidelines to ensure consistant approaches to annotation.
- Gene Ontology Annotation and Term Development
We use the GOA curation tool to associate Gene Ontology terms to gene products including proteins, RNAs and macromolecular complexes. The data we produce is incorporated into the GOA and GO Consortium databases. Annotations contributed by UCL are attributed to BHF-UCL, ParkinsonsUK-UCL, ARUK-UCL or SynGO-UCL and also many of the HGNC GO annotations were created by the HGNC while based at UCL.
- Annotation of Molecular Interactions
The creation of protein interaction networks is an essential step towards the unravelling of the complex molecular interactions in living organisms. Therefore, the UCL annotation team is contributing experimentally verified protein interaction data to two databases:
- We use the IntAct editing tool to capture protein interactions at a very detailed level as described in the IMEx guidelines. These annotations are directly incorporated into the IntAct database, from where they are exported to the IMEx Consortium database.
- Protein-protein and microRNA-mRNA interactions are also submitted to the Gene Ontology Consortium (GOC) database using the GOA curation tool and can be accessed via the QuickGO website.
New! All of these datasets ("bhf-ucl", "EBI-GOA-nonIntAct" and "EBI-GOA-miRNA"), can also be accessed using the Cytoscape software via PSICQUIC.
- Contributing to Annotation Guidelines
The UCL team is actively involved the formulation of annotation guidelines, as part of the Annotation team in the GO Consortium.
Topic Details Gene expression and transcription curation guidelines Rachael and Barbara created a decision tree based on experimental assays used to measure gene expression and transcription to assist curators in choosing the appropriate GO terms for the evidence provided. Ruth is working with GREEKC to improve the representation of transcription processes in several online resources, including the Gene Ontology Evidence code guidelines Rachael provided several use case examples for the IGI evidence code documentation and Rebecca has initiated a change to the IC evidence code application. Capturing non-GOC contributions Ruth was involved in discussions to create GOC webpages that encourage expert scientist to suggest improvements to the GO and submit GO annotations. Protein complexes Nancy participated in two protein complex working group (WG); the complex annotation WG and the complex ontology WG. The groups discuss the various aspects of creating and annotating protein complexes. Annotation extension Ruth, Rachael and Rebecca were involved in discussions about the use of this field and the associated relationships. Creating wiki pages for each relation to document their application. microRNA Ruth chaired discussions on guidelines for the annotation of microRNAs. Rachael has created a miRNA curation manual in consultation with the GOC and miRNA experts. Response to Ruth and Varsha were part of the 'response to' working group formulating guidelines to standardise the use of 'response to' GO terms. Regulation Ruth and Varsha were part of the 'regulation' working group creating guidelines to standardise the use of 'regulation' GO terms. Downstream processes Varsha and Rachael Huntley (previously GOA) co-chaired the 'downstream process' working group, to formulate guidelines for the annotation of downstream processes. Binding Ruth was a member of the binding working group which formulated guidelines for the useage of binding terms.
 Close
Close

