Clinical samples of formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue, fat aspirates or untreated tissue are received following referral to the NAC or through the Fibril typing service.
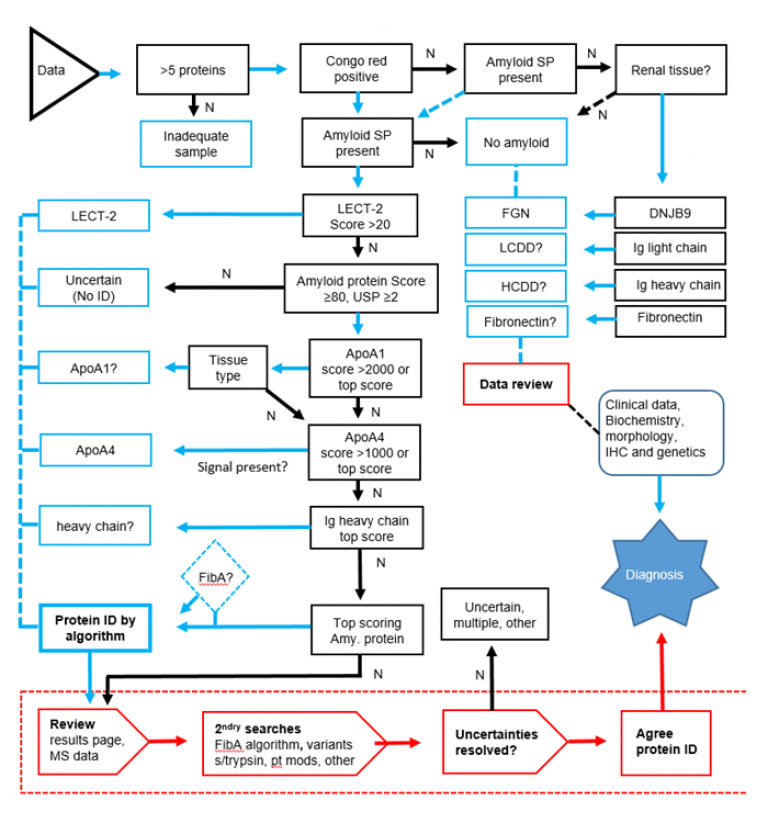
Following staining and immunohistochemistry, Congo red-positive (amyloid) material is selected by laser capture dissection (LCD), and analysed by a proteomics approach using the Mascot search engine to identify the amyloidogenic protein(s). Variant and other searches are conducted as appropriate. The clinical and proteomic databases are linked, and we use a simple algorithm to automatically identify the pathogenic amyloid protein (3).
Amyloidogenic proteins identified in our patient database (3): apolipoproteins A1, A4, C2, C3, ANP, fibrinogen Aα chain, gelsolin, immunoglobulin light chains (lambda and kappa) and heavy chain, insulin, leukocyte cell-derived chemotaxin-2, lysozyme, b2-microglobulin, semenogelin, serum amyloid A, transthyretin.
Proteomics can also identify non-amyloid fibrillary glomerulonephritis from the DNJB9 signature (4).
Clinical proteomics data are reviewed, together with histological, genetic and clinical presentation, at a weekly multidisciplinary team meeting by both clinical and scientific research staff.
The NAC proteomics algorithm (3)
 Close
Close

