The science behind the research
Kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) materials have direct band gap energies ranging from 1.0 eV to 1.5 eV and high absorption coefficients (>104 cm−1), which make them a feasible option for photovoltaic thin film technologies. Compared to CIGS, CZTS-based materials consist of earth-abundant elements and represent promising candidates for low-cost and high-efficiency thin film solar cells. A cutting edge Electrostatic Assisted Vapour Deposition (ESAVD) method has been developed to obtain high efficiency CZTS thin films with high uniformity and no secondary phases under non-vacuum conditions.
Ongoing research
Our most recent results have shown that CZTS solar cells fabricated by ESAVD can reach efficiency of 6.5%. This has been achieved by optimizing the processing steps and by incorporating alkaline metal ions in appropriate amounts.
| Fig 1. SEM cross section of CZTS solar cell |
 |
| Fig 2. IV curve for CZTS solar cells |
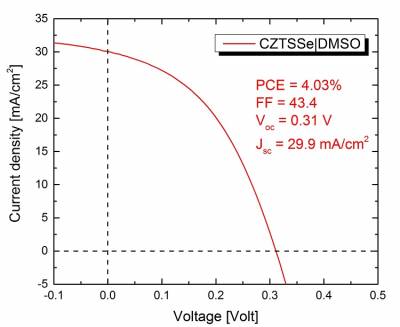 |
Recent publications
- Nazligul, A. S., Wang, M., & Choy, K. L. (2020). Recent development in earth-abundant kesterite materials and their applications. Sustainability, 12, (12) 5138. doi:10.3390/su12125138
- Liu, J. P., Choy, K. L., Placidi, M., López-García J., Saucedo, E., Colombara D., & Robert, E. (2015). Fabrication and characterization of kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 thin films deposited by electrostatic spray assisted vapour deposition method. Physica Status Solidi A, 212, (1), 135-139. doi: 10.1002/pssa.201431374
Conference presentations
- Altamura, G., Wang, M., & Choy, K.L. (2015). Environmentally friendly and non-vacuum Electrostatic Spray Assisted Vapor Deposited Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 using different non-toxic solvents. EMRS Spring meeting 2015. Lille, France.
 Close
Close

