Condensed Matter & Materials Physics (CMMP)
Research Highlights

Disorder-Induced Transition from Transient Quantum Delocalization to Charge Carrier Hopping Conduction in a Nonfullerene...
...Acceptor Material Ljiljana Stojanović, Jack Coker, Samuele Giannini, Giacomo Londi, Anders S. Gertsen, Jens Wenzel Andreasen, Jun Yan, Gabriele D’Avino, David Beljonne, Jenny Nelson, and Jochen Blumberger
In organic semiconductors, charge carriers may form delocalized or localized quasiparticles depending on molecular properties and environmental effects. Here, it is shown how structural and electrostatic disorder induce localization.
Stojanović, L et al. Disorder-Induced Transition from Transient Quantum Delocalization to Charge Carrier Hopping Conduction in a Nonfullerene Acceptor Material. Phys Rev X 14, 021021 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevX.14.021021
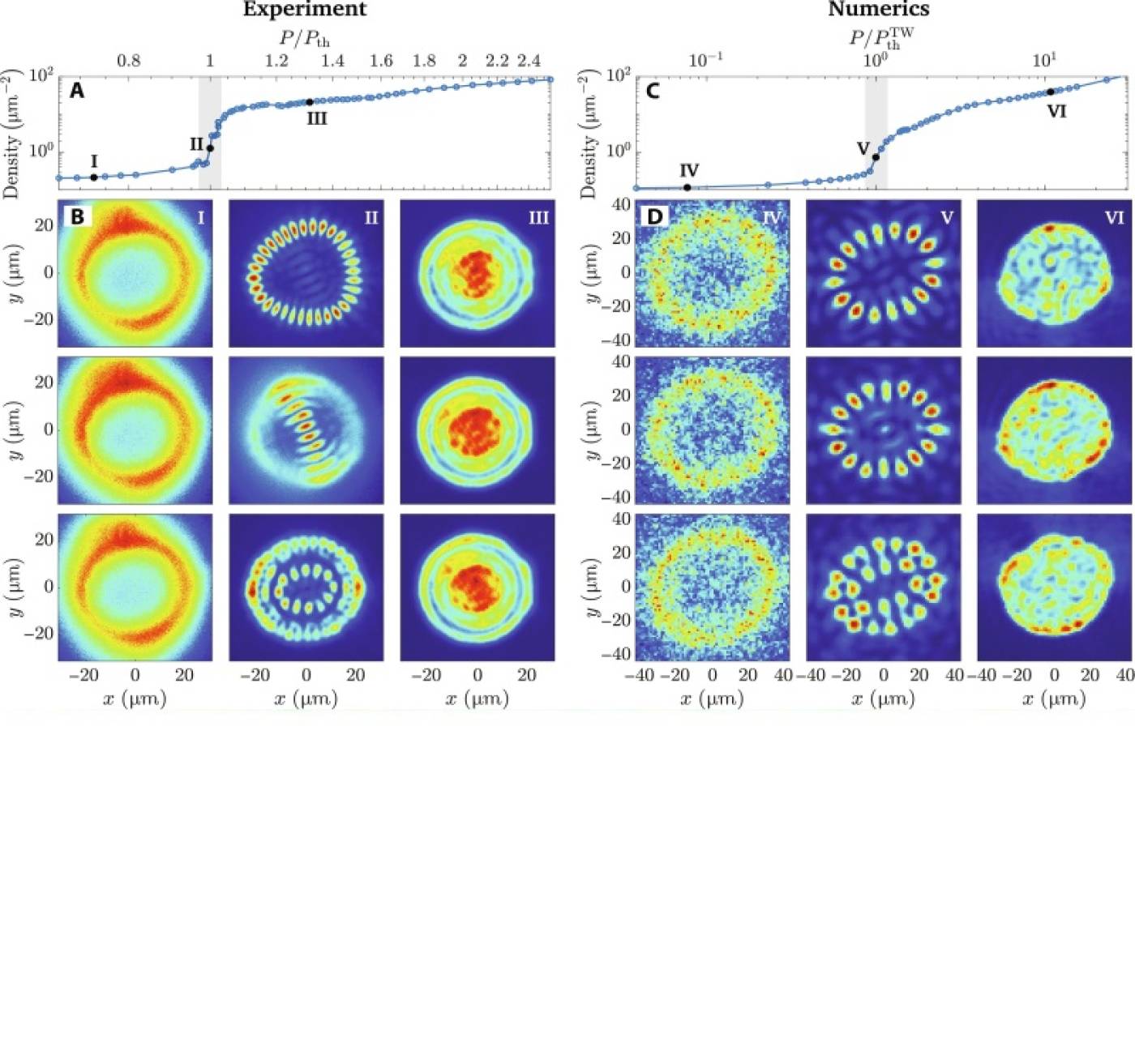
Critical fluctuations in a confined driven-dissipative quantum condensate
Hassan Alnatah, Paolo Comaron, Shouvik Mukherjee, Jonathan Beaumariage, Loren N Pfeiffer, Ken West, Kirk Baldwin, Marzena Szymańska, and David W Snoke
Phase fluctuations determine the low-energy properties of quantum condensates. However, at the condensation threshold, both density and phase fluctuations are relevant. The manifestation of a critical quantum state competition unlocks possibilities for the study of condensate formation while linking to practical realizations in photonic lasers.
Hassan Alnatah et al. Critical fluctuations in a confined driven-dissipative quantum condensate. Sci Adv 10, eadi6762 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adi6762

EUV-induced hydrogen desorption as a step towards large-scale silicon quantum device patterning
Procopios Constantinou, Taylor J. Z. Stock, Li-Ting Tseng, Dimitrios Kazazis, Matthias Muntwiler, Carlos A. F. Vaz, Yasin Ekinci, Gabriel Aeppli, Neil J. Curson, and Steven R. Schofield
Unleashing the power of extreme-ultraviolet (EUV) light, scientists from UCL and the Paul Scherrer Institute, EPFL, and ETHZ in Switzerland have devised an innovative technique for patterning hydrogen-terminated silicon, charting a course towards the large-scale fabrication of quantum devices in silicon.
Procopios Constantinou et al. EUV-induced hydrogen desorption as a step towards large-scale silicon quantum device patterning. Nat Commun 15, 694 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-44790-6
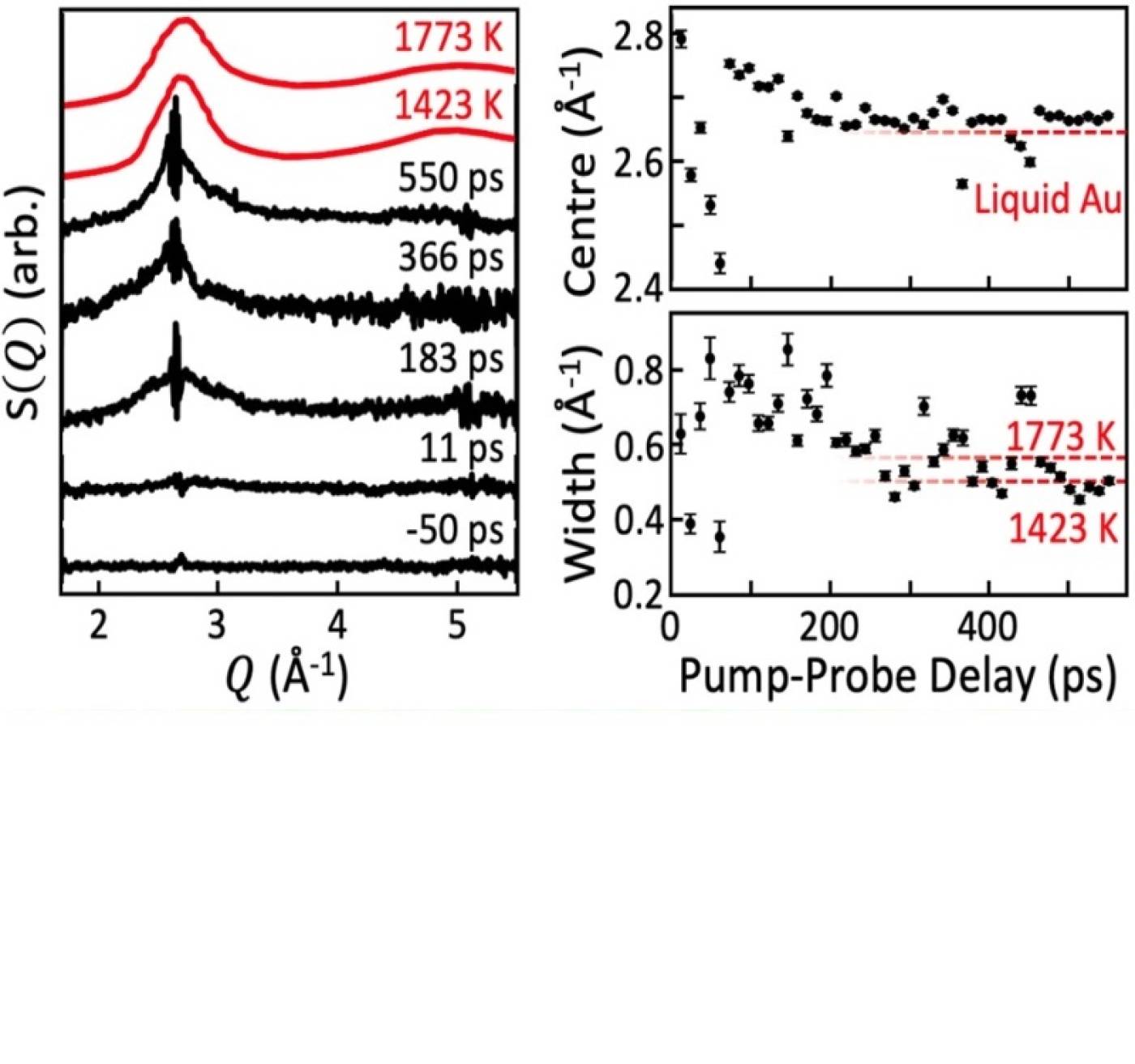
Emergence of liquid following laser melting of gold thin films
Ian K. Robinson, Jack P. Griffiths, Robert Koch, Tadesse A. Assefa, Ana F. Suzana, Yue Cao, Sungwon Kim, Dongjin Kim, Heemin Lee, Sunam Kim, Jae Hyuk Lee, Sang-Youn Park, Intae Eom, Jaeku Park, Daewoog Nam, Sangsoo Kim, Sae Hwan Chun, Hyojung Hyun, Kyung sook Kim, Ming Lu, Changyong Song, Hyunjung Kim, Simon J. L. Billinge, and Emil S. Bozin
Laser metling of gold thin films were exemined using single shots of X-rays from a free-electron laser. The evolution of the extractied diffuse scattering of the liquid shows structural realxations over the first150 picoseconds.
Ian K. Robinson et al. Emergence of liquid following laser melting of gold thin films. IUCrJ 10, 656-661 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1107/S2052252523009363
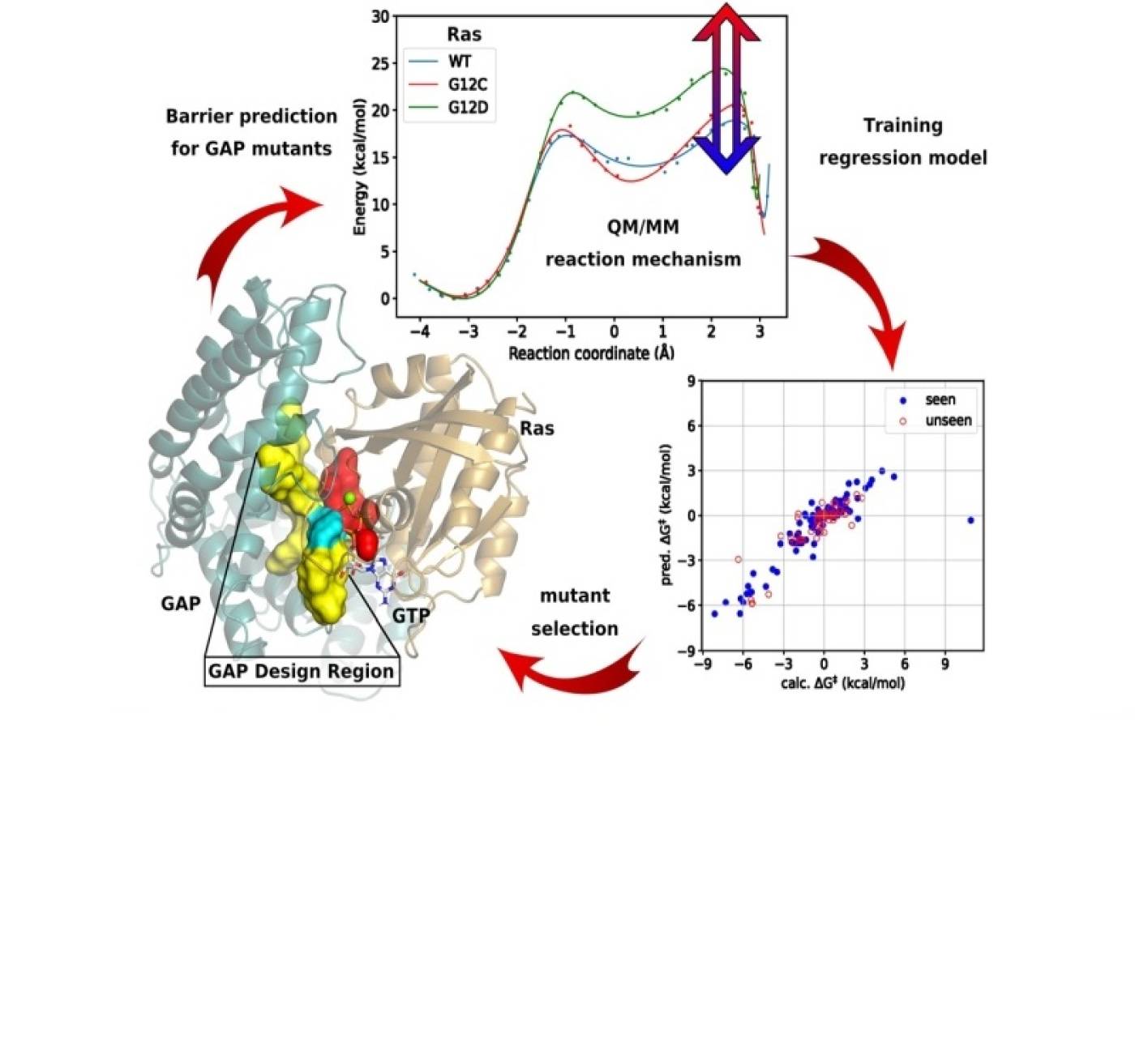
Mechanism-Based Redesign of GAP to Activate Oncogenic Ras
Dénes Berta, Sascha Gehrke, Kinga Nyíri, Beáta G. Vértessy, and Edina Rosta
QM/MM simulations reveal the detailed mechanism of GTP hydrolysis and the negative effect of mutations in cancer. Exploiting the atomistic understanding, we deviced a computational screening protocol, sped-up with machine learning, capable of protein engineering to restore the lost activity and paving the way for a novel therapeutic approach.
Berta, D et al. Mechanism-Based Redesign of GAP to Activate Oncogenic Ras. J Am Chem Soc 2023, 145, 37, 20302–20310. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c04330
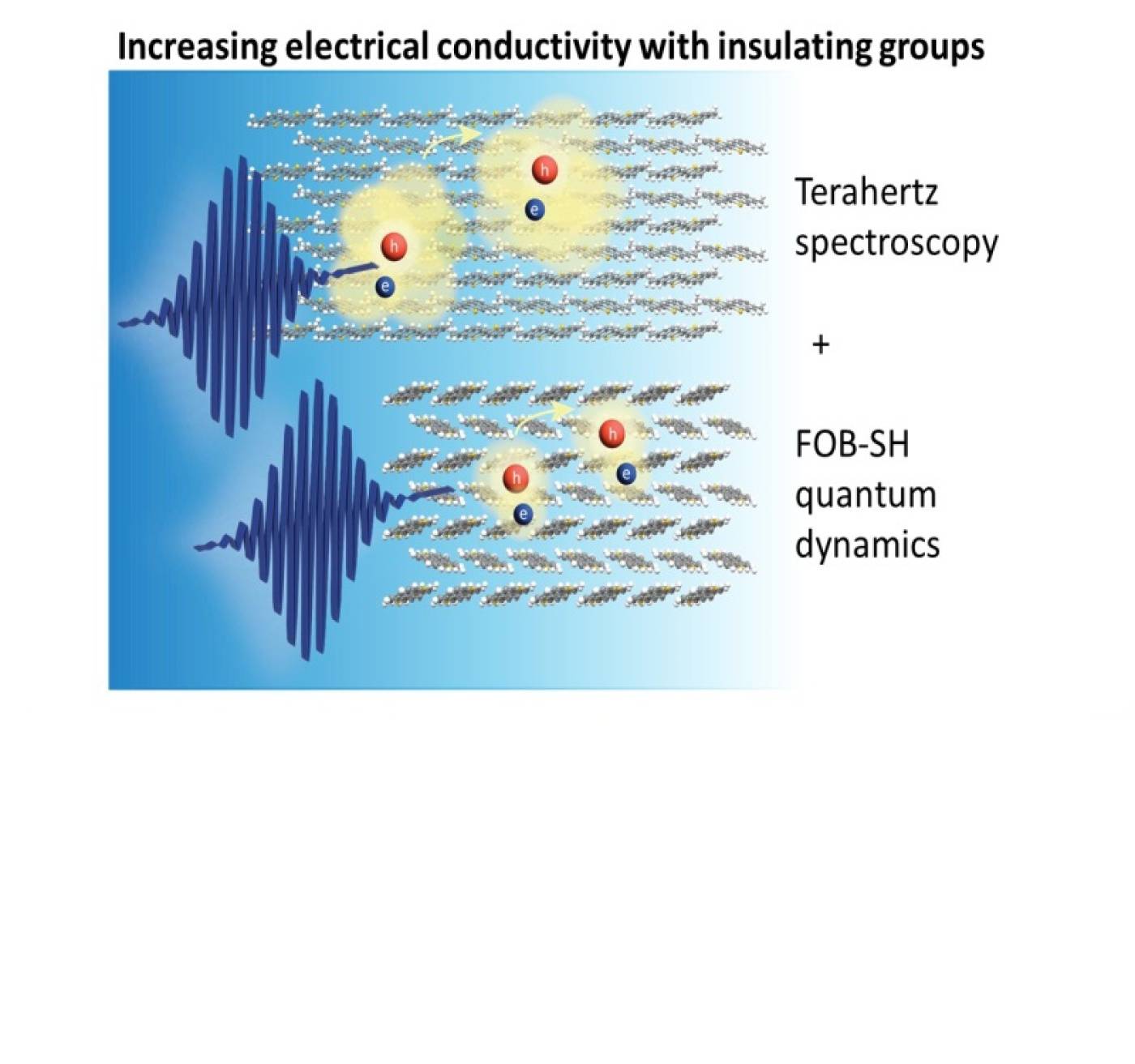
Transiently delocalized states enhance hole mobility in organic molecular semiconductors
Samuele Giannini, Lucia Di Virgilio, Marco Bardini, Julian Hausch, Jaco J. Geuchies, Wenhao Zheng, Martina Volpi, Jan Elsner, Katharina Broch, Yves H. Geerts, Frank Schreiber, Guillaume Schweicher, Hai I. Wang, Jochen Blumberger, Mischa Bonn and David Beljonne
By combining terahertz photoconductivity measurements with non-adiabatic molecular dynamics simulation developed in Jochen Blumberger's group, Giannini et al show that charge transport in two organic semiconductors is mediated by holes surfing on extended electronic states with a temperature-dependent mobility that provides a sensitive fingerprint for the underlying density of states.
Giannini, S., Di Virgilio, L., Bardini, M. et al. Transiently delocalized states enhance hole mobility in organic molecular semiconductors. Nat Mater (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41563-023-01664-4
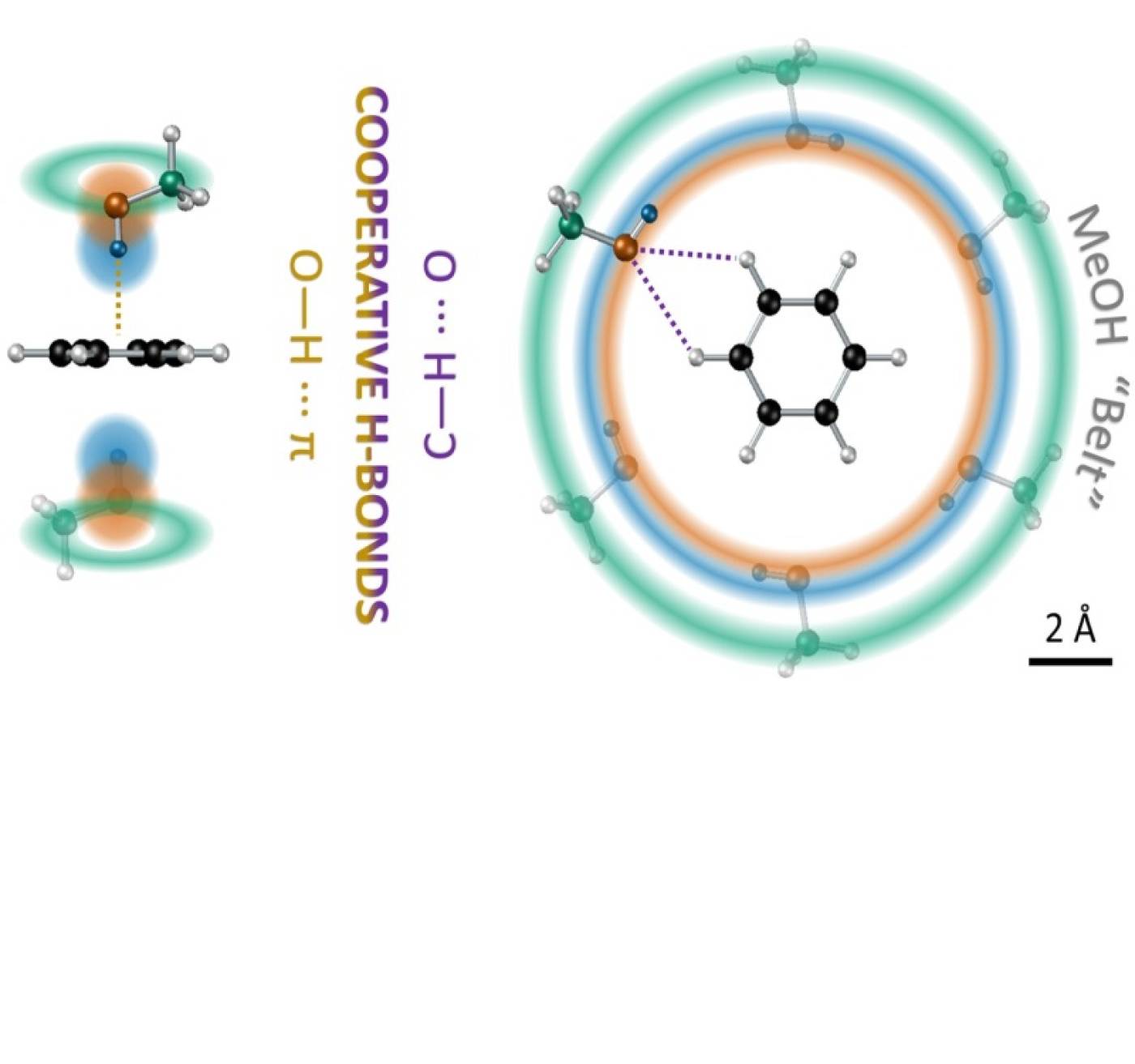
Strong structuring arising from weak cooperative O-H···π and C-H···O hydrogen bonding in benzene-methanol solution
Camilla Di Mino, Andrew G. Seel, Adam J. Clancy, Thomas F. Headen, Támas Földes, Edina Rosta, Andrea Sella, and Neal T. Skipper
This research sheds light on the weak (non-covalent) intermolecular interactions that occur in a liquid mixture: cooperation plays an important role!
Di Mino, C, Seel, AG, Clancy, AJ et al. Strong structuring arising from weak cooperative O-H···π and C-H···O hydrogen bonding in benzene-methanol solution. Nat Commun 14, 5900 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-41451-y
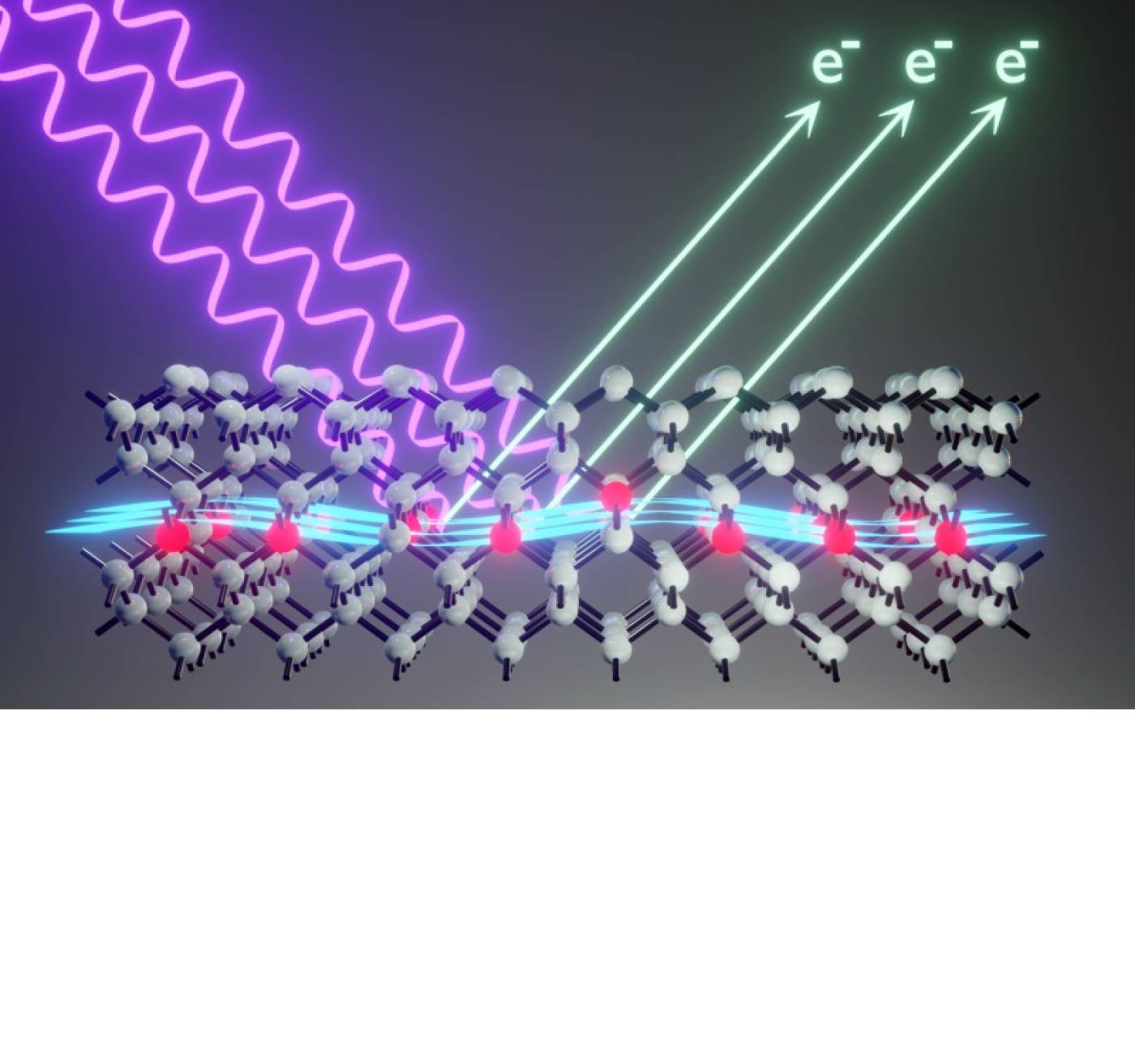
Unveiling ultra-thin electron liquids in silicon
Constantinou, P., Stock, T. J. Z., Crane, E., Kölker, A., van Loon, M., Li, J., Fearn, S., Bornemann, H., D'Anna, N., Fisher, A. J., Strocov, V. N., Aeppli, G., Curson, N. J., Schofield, S. R.
Soft X-rays enable UCL and Swiss scientists to visualise non-invasively the electronic properties of ultra-thin dopant layers buried within semiconductor wafers. The ability to access this previously hidden information will give a boost to the design and development of quantum-electronic devices.
Constantinou, P. et al. Momentum-Space Imaging of Ultra-Thin Electron Liquids in δ-Doped Silicon. Adv. Sci. 2023, 2302101. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202302101
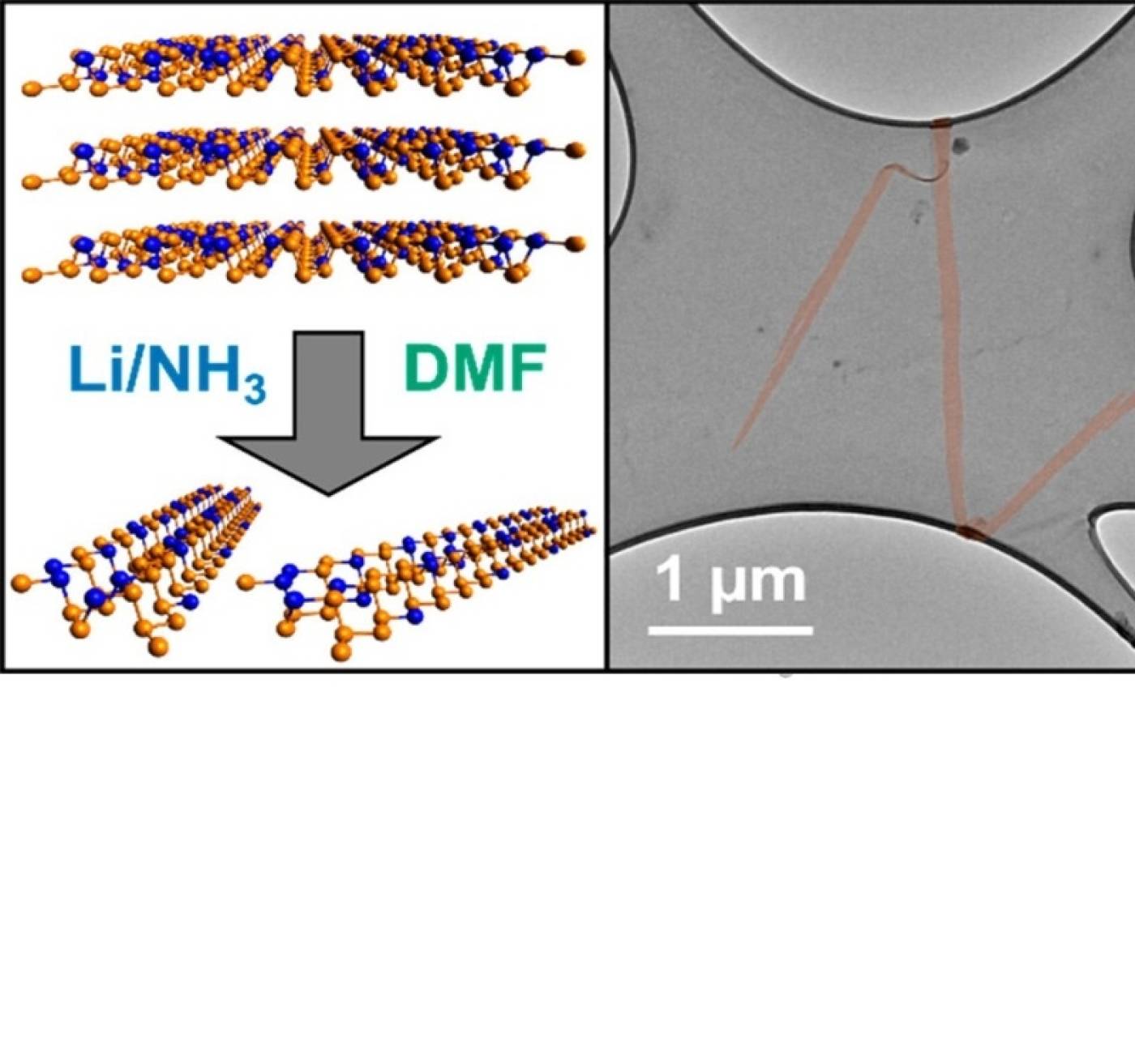
Production of Magnetic Arsenic–Phosphorus Alloy Nanoribbons with Small Band Gaps and High Hole Conductivities
Feng Fei Zhang, Eva Aw, Alexander G. Eaton, Rebecca R. C. Shutt, Juhwan Lim, Jung Ho Kim, Thomas J. Macdonald, Cesar III D. L. Reyes, Arjun Ashoka, Raj Pandya, Oliver D. Payton, Loren Picco, Caroline E. Knapp, Furio Corà, Akshay Rao, Christopher A. Howard, and Adam J. Clancy
In this work, we created one-atom-thick ribbons made of phosphorus alloyed with arsenic. These nanoscale materials have a number of unique properties that are both of fundamental interest and potential use in batteries, supercapacitors and solarcells.
Feng Fei Zhang et al. Production of Magnetic Arsenic–Phosphorus Alloy Nanoribbons with Small Band Gaps and High Hole Conductivities. J Am Chem Soc 2023, 145, (33), 18286-18295. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c03230
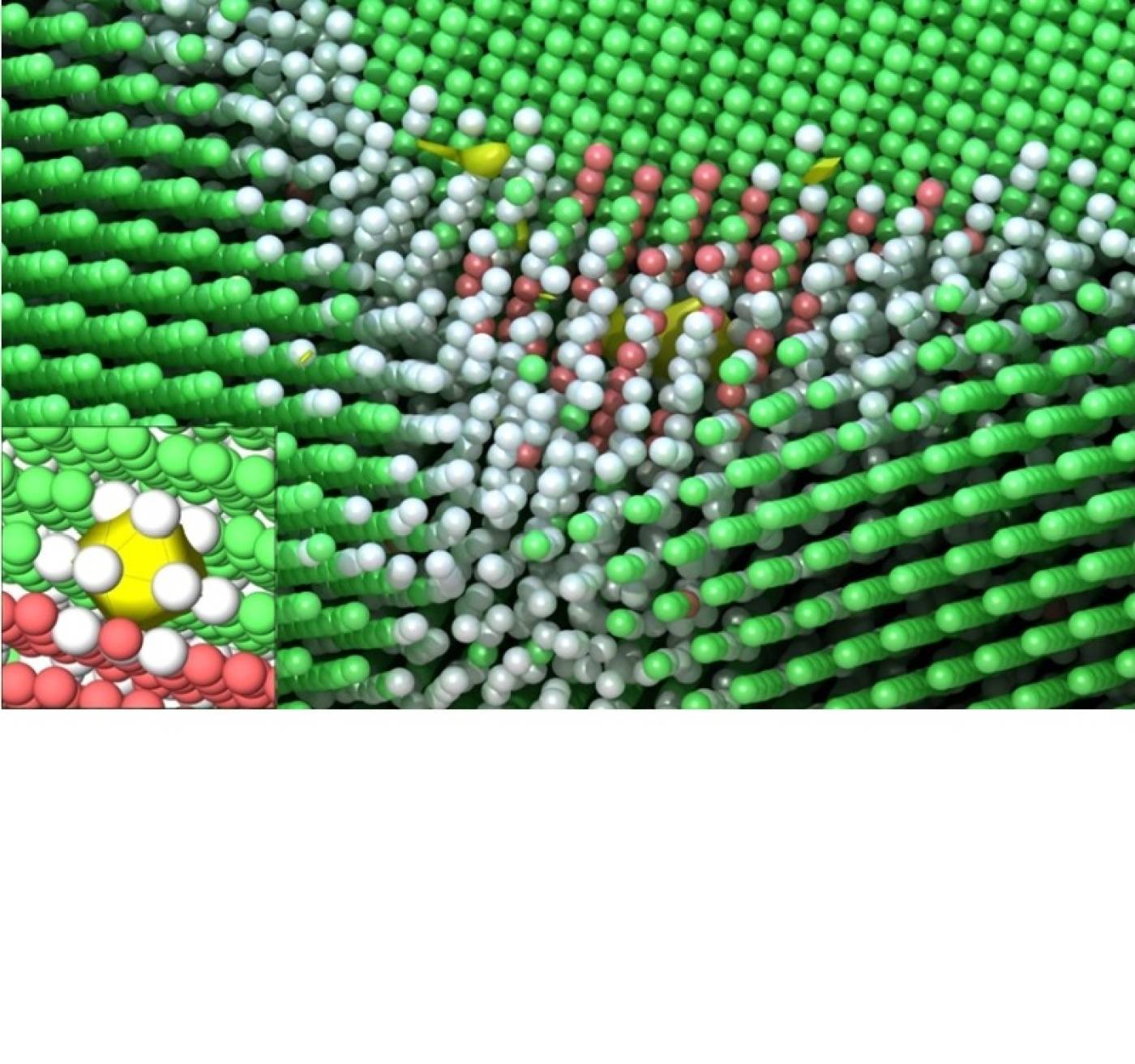
Structure and Migration Mechanisms of Small Vacancy Clusters in Cu: A Combined EAM and DFT Study
Vasileios Fotopoulos, David Mora-Fonz, Manuel Kleinbichler, Rishi Bodlos, Ernst Kozeschnik, Lorenz Romaner, and Alexander L. Shluger
When multi-grain metals are subjected to heat and/or stress, defects called vacancies—small empty spaces (yellow surface)—are formed close to grain boundaries (white balls) and defectuous regions (red balls), affecting the material’s mechanical strength.
Fotopoulos, V et al. Structure and Migration Mechanisms of Small Vacancy Clusters in Cu: A Combined EAM and DFT Study. Nanomaterials 2023, 13(9), 1464. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13091464
 Close
Close

