Complementary spin-Hall and inverse spin-galvanic effect torques in a ferromagnet/ semiconductor bilayer
19 November 2016
T.
 D. Skinner, K. Olejník, L. K. Cunningham, H. Kurebayashi, R. P. Campion, B. L. Gallagher, T. Jungwirth, & A. J. Ferguson. Nature Communications 6, 6730 (2015)
D. Skinner, K. Olejník, L. K. Cunningham, H. Kurebayashi, R. P. Campion, B. L. Gallagher, T. Jungwirth, & A. J. Ferguson. Nature Communications 6, 6730 (2015)
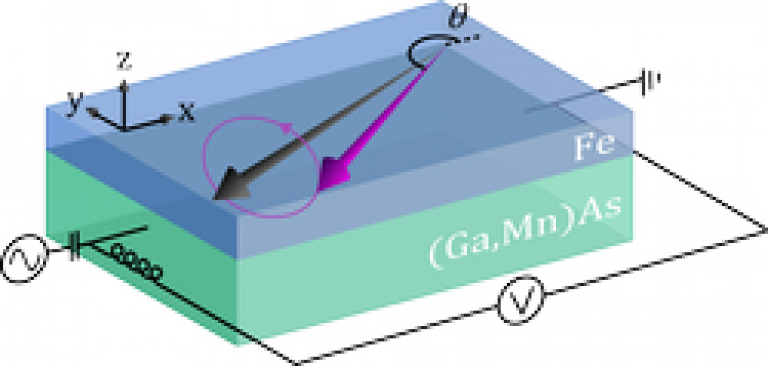
Electrically-induced torques observed in ferromagnet/paramagnet metal bilayers have been attributed to separate mechanisms involving the spin-Hall effect and inverse-spin galvanic effect. In this paper, the metal paramagnet is replaced with a semiconductor paramagnet. Using an electrically driven ferromagnetic resonance technique, the current-induced torques are measured. As the semiconductor produces a different symmetry inverse spin-galvanic effect to the metal bilayers, for the first time the contributions of the two mechanisms can be disentangled.
 Close
Close

