Iron in brain shows cognitive decline in people with Parkinson’s
21 February 2020
A cutting-edge MRI technique to detect iron deposits in different brain regions can track declines in thinking, memory and movement in people with Parkinson’s disease, finds a new UCL-led study.
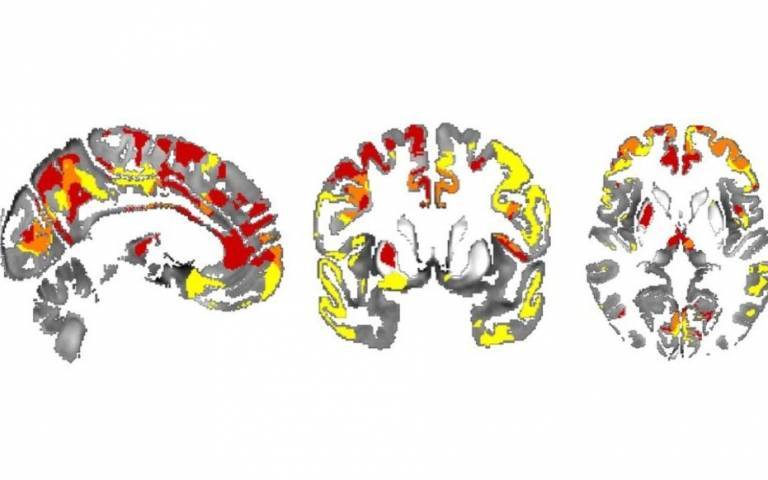
The findings, published in the Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, suggest that measures of brain iron might eventually help predict which people with Parkinson’s will develop dementia.
“Iron in the brain is of growing interest to people researching neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and dementias. As you get older, iron accumulates in the brain, but it’s also linked to the build-up of harmful brain proteins, so we’re starting to find evidence that it could be useful in monitoring disease progression, and potentially even in diagnostics,” said the study’s lead author, Dr Rimona Weil (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology).
The study involved 97 people with Parkinson’s disease, who had been diagnosed within the last 10 years, along with 37 people without the condition, as a control (comparison) group. They were tested for their thinking and memory as well as for their motor function.
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive condition of brain degeneration resulting in tremors, stiffness and slowness of movement. Close to 50% of people with the condition end up developing dementia, but the timing and severity vary substantially.
Currently there are no reliable measures to track Parkinson’s progression in the brain, so clinicians rely on monitoring symptoms. Conventional brain imaging fails to track progression until quite a late stage, when large-scale brain volume loss can be detected.
Iron accumulates in people’s brains as part of the normal ageing process, partly due to increased permeability in the blood-brain barrier. Excess iron can have toxic effects leading to proteins being irreversibly modified. Recent studies have found that when proteins linked to Alzheimer’s disease (amyloid and tau, which are also linked to Parkinson’s dementia) build up, iron also accumulates in the affected brain areas.
In the current study, researchers used a new technique, called quantitative susceptibility mapping,* to map iron levels in the brain based on MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scans. They found that iron accumulation in the hippocampus and thalamus brain regions was associated with poor memory and thinking scores. Iron in the putamen brain region was associated with poor movement scores, suggesting a more advanced stage of the disease.
In Parkinson’s disease, the hippocampus and thalamus are known to be associated with thinking and memory, and the putamen with movement scores, so the researchers say it’s very promising that iron deposition was specifically detected in those areas.
The findings suggest that iron deposition could be valuable to track if a treatment is working in a clinical trial, and might eventually be helpful for early diagnosis of Parkinson’s or other neurodegenerative diseases.
Dr Weil has previously found in a 2019 study** that a suite of vision tests may be helpful to predict cognitive decline in Parkinson’s. She and her colleagues hope that further research will determine if the vision tests and iron measures could be helpful to predict which people with Parkinson's are likely to develop dementia.
First author, PhD student George Thomas (UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology), said: “It’s really promising to see measures like this which can potentially track the varying progression of Parkinson’s disease, as it could help clinicians devise better treatment plans for people based on how their condition manifests.”
Co-author Dr Julio Acosta-Cabronero (Tenoke Ltd. and Wellcome Centre for Human Neuroimaging, UCL) added: "We were surprised at how well the iron levels measured in different regions of the brain with MRI were correlated with cognitive and motor skills. We hope that brain iron measurement could be useful for a wide range of conditions, such as to gauge dementia severity or to see which brain regions are affected by other movement, neuromuscular and neuroinflammatory disorders, stroke, traumatic brain injury and drug abuse.”
The researchers are now following up the same study participants to see how their disease is progressing, whether they develop dementia, and how such measures correlate with changes in iron levels over time.
The study was supported by Wellcome, the National Institute for Health Research, the Medical Research Council, Parkinson’s UK, Movement Disorders Society, ESRC, and the Cure Parkinson’s Trust.
UCL dementia research gets funding boost
Neuroscience research at UCL has received a new boost with a £5 million grant from the Garfield Weston Foundation, supporting the planned development of a new world-leading neuroscience centre at UCL. The state-of-the-art new building*** will house over 500 neuroscientists from the UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology as well as the research hub and operational headquarters of the UK Dementia Research Institute (UK DRI) – a nationwide collaboration to revolutionise the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative disorders. It will also house outpatient consulting and an MRI suite for the UCLH National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery.
The £5 million donation from The Foundation is their largest gift to UCL to date. They will be naming the Weston Conference Centre in the new building on Grays Inn Road, which will provide facilities to connect scientists and welcome visiting collaborators from across the UK and the world. It will be a crucial part of the new building which is a physical embodiment of UCL’s commitment to translational research and collaborative working to find solutions to some of society’s most devastating neurodegenerative diseases.
Links
- Research paper in JNNP
- Dr Rimona Weil’s academic profile
- UCL Queen Square Institute of Neurology
- Wellcome Centre for Human Neuroimaging at UCL
- * Quantitative susceptibility mapping estimates the concentration of elements such as iron or calcium by measuring the magnetic susceptibility of different tissues in the brain; areas with more iron would have greater magnetic susceptibility. This is the first time the technique has been used across the whole brain to track cognitive changes in Parkinson’s disease.
- ** 2019 study: Simple eye tests to predict Parkinson’s-linked dementia
- *** Read more about the new home for UCL Neuroscience: New world-leading facility for UCL Neuroscience gains planning approval
- The Garfield Weston Foundation donate £5 million to world-leading neuroscience centre at UCL
- Garfield Weston Foundation
- Media coverage
Image
- Areas with iron accumulation in the brains of people with Parkinson's, correlated with risk of cognitive decline. Credit: George Thomas et al
Media contact
Chris Lane
Tel: +44 (0)207 679 9222
Email: chris.lane [at] ucl.ac.uk
 Close
Close

