Biodiversity protects against invasions of non-native tree species
23 August 2023
For the first time, researchers combined human and ecological factors to analyse the global scale of non-native tree species invasions. Human activity in hotspots of global trade, such as maritime ports, is linked to an increased likelihood of non-native tree species invasions.

However, a high diversity of native tree species can help to curb the intensity of such invasions.
In brief
- First global study reveals the extent of non-native tree invasions around the world.
- Proximity to human activity is a dominant factor in determining where invasions occur across the globe.
- Native biodiversity can mitigate the extent of non-native tree species invasions.
For centuries, human activity has intentionally or unintentionally driven the spread of plant species to areas far outside their native habitat. On average, about 10 percent of non-native species worldwide become invasive, often causing large ecological and economic consequences for affected regions.
For the first time, a global team of researchers, led by ETH Zurich, have explored which regions on Earth are most vulnerable to non-native tree invasions. The study, published in the journal Nature, combined human, and ecological factors to assess the drivers of tree invasion occurrence and severity across the globe.
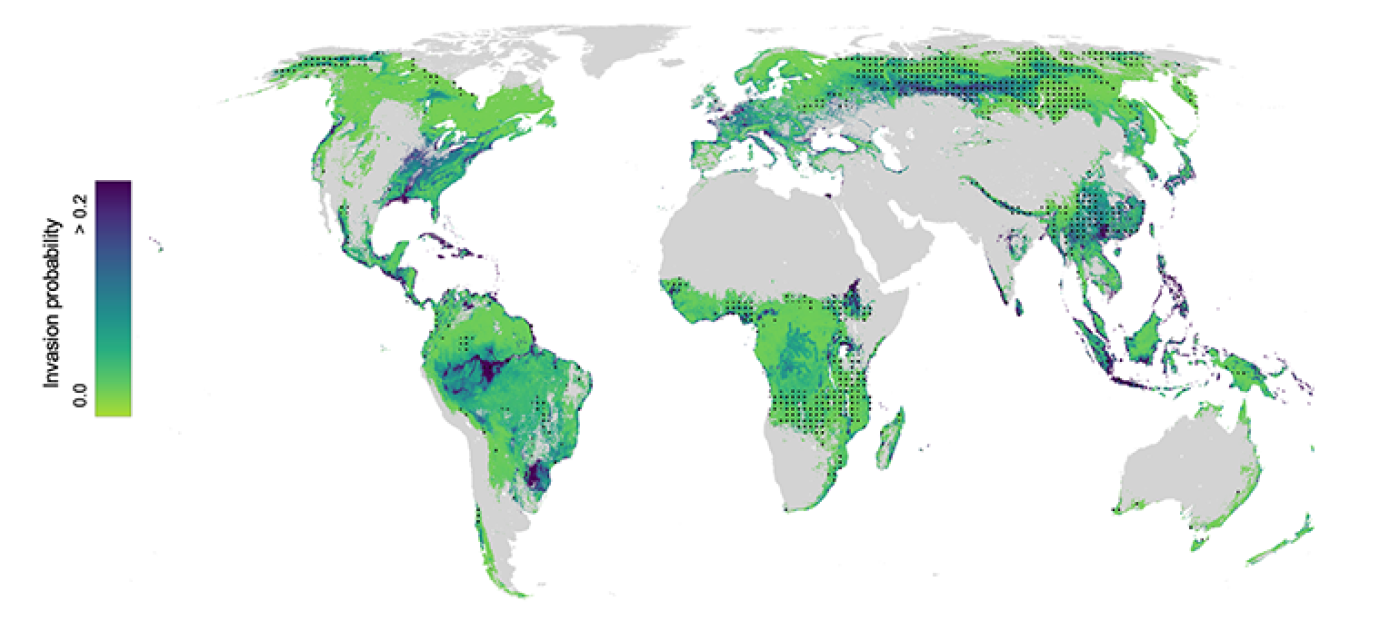
Image credit: ETH Zurich
Ecological factors determine severity
The study reveals that proximity to human activity – especially maritime ports – emerges as a dominant factor driving the likelihood of invasion. Ports handle tonnes of goods including plants or seeds from all corners of the globe. The colonization pressure exerted by plant material is, therefore, very high in these regions of high human activity. The closer a forest is to a port, the higher the risk of invasion.
However, ecological factors determine the severity of invasion. Most importantly, native biodiversity helps to buffer the intensity of these invasions. In diverse forests, when most of the available niches are filled by native species, it becomes harder for non-native tree species to spread and proliferate.
The ecological strategy of the invading species is also important in determining which types of trees can invade in different regions. In harsh regions with extreme cold or dry conditions, the researchers found that non-native tree species must be functionally similar to native species to survive in these harsh environments. However, in locations with moderate conditions, non-native trees must be functionally dissimilar to native species in order to survive by functionally differentiating themselves, the non-native species avoid intense competition with native trees for important resources such as space, light, nutrients, or water.
Native biodiversity is a strong defence
Overall, the study highlights the importance of native tree diversity in helping to limit the severity of these invasions. “We found that native biodiversity can limit the severity or intensity of non-native tree species invasions worldwide,” says Camille Delavaux, lead author of the study. “This means that the extent of invasion can be mitigated by promoting greater native tree diversity.”
“By helping to insulate ecosystems against invasive species, this work shows that native biodiversity plays a critical role in ensuring healthy, resilient forests,” says Associate Professor Daniel Maynard (UCL Division of Biosciences), the senior scientist on the study and formerly a researcher at the Crowther Lab at ETH Zurich.
The findings have direct relevance for efforts to manage ecosystems in the fight against biodiversity loss across the globe. “By identifying regions that are most vulnerable to invasion, this analysis is useful for designing effective strategies to protect global biodiversity,” says ETH Zurich professor, Thomas Crowther. A large consortium of researchers took part in the study and collected valuable data. “Without the incredible cooperation of scientists around the world, this global perspective would not have been possible.”
Invasive species in focus worldwide
Indeed, the findings are significant for biodiversity conservation efforts worldwide. One key goal of the global biodiversity framework adopted at COP 15 in Montreal in 2022 is to prevent the establishment and spread of potentially invasive species. This global analysis of non-native tree species aims to contribute to the findings of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES), which is expected to highlight the substantial impact of invasive species on biodiversity loss in their upcoming status report.
“This global understanding of non-native tree distributions can help countries to prioritise decision making in efforts to halt and reverse the loss of biodiversity,” Crowther emphasises.
Examples of non-native tree species across the globe
The study identifies 250 non-native tree species worldwide. Here are just five examples:
- Black Locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) - originated in North America; introduced to Europe 400 years ago and used extensively to stabilize terrain along the Gotthard railway; flagged as an invasive species in Switzerland.
- Osage Orange (Maclura pomifera) – native to the south-central U.S.; historically planted across the continental U.S. and southern Canada for agriculture, notably as a natural fence.
- Spruce (Picea abies) - originates from Europe and planted extensively in North America; this species often renders surrounding soil acidic and develops a dense canopy, making it difficult for native species to compete.
- Scots Pine (Pinus sylvestris) - distributed from Europe to Siberia; introduced in North America and New Zealand; several Pinus species are thought to invade thanks to the cointroduction of their mycorrhizal symbionts.
- God Tree (Ailanthus altissima) - originated in China, Korea, and Taiwan; present on all continents except Antarctica; spreads efficiently by underground runners and can damage structures; flagged as an invasive species in Switzerland.
- Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis) - west coast of North America, introduced to Europe in the 19th century as a timber tree. Sitka spruce plantations have become the dominant forest type in the UK and Ireland.
- Eucalypts (Eucalyptus sp.) - originates from Australia, planted in southern Europe and South Africa, among other places, for its fast growth and good timber quality. Provides no habitat for native wildlife, aggressively displaces native species, and dries soils to depths.
Further information:
- Dr Daniel Maynard
- ETH Zurich
- ETH Zurich article: "Biodiversity protects against invasions of non-native tree species"
- Nature paper: "Native diversity buffers against severity of non-native tree invasions globally"
Media contacts:
- Camille Delavaux, Lead Scientist in the Crowther Lab at ETH Zurich and first author of this Nature publication: camille.delavaux@usys.ethz.ch
- Crowther Lab press team: press@crowtherlab.com
Author:
ETH Zurich Editorial Team
Main image:
Manoa Valley in Hawaii. Image by Leland Werden of the Crowther Lab.
 Close
Close

