The BEST1 gene gives instruction to make the BEST1 protein.
Proteins are complex molecules that do the work in cells, playing a role in almost every biological process. Proteins are required for cell structure and function and they help regulate processes in our tissues and organs. The exact structure and function of the BEST1 protein has been a cause for much debate in previous years, with most scientists suggesting it may have multiple purposes within the RPE.
BEST1 belongs to the Bestrophin protein family and is made up of 585 amino acids (the building blocks of proteins) and extensive research has shown that it is located exclusively in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) of the eye. Studies have shown that BEST1 protein is located at the basolateral membrane of the RPE I.e. along the base and up the sides of the RPE.
BEST1 is believed to act as a channel protein, controlling the flow of chloride ions (small atoms with an electric charge) through the basolateral membrane of the RPE cell. The BEST1 channel acts as a gate, which is only opened when a calcium ion binds to it. BEST1 is therefore known as a calcium-activated chloride channel.
Chloride is an essential electrolyte that helps to maintain fluid balance in the body, it also plays a role in the generation of electrical signals in cells. The controlled movement of chloride ions by BEST1 could act to regulate the transport of fluid in and out of cells or generate an electrical message.
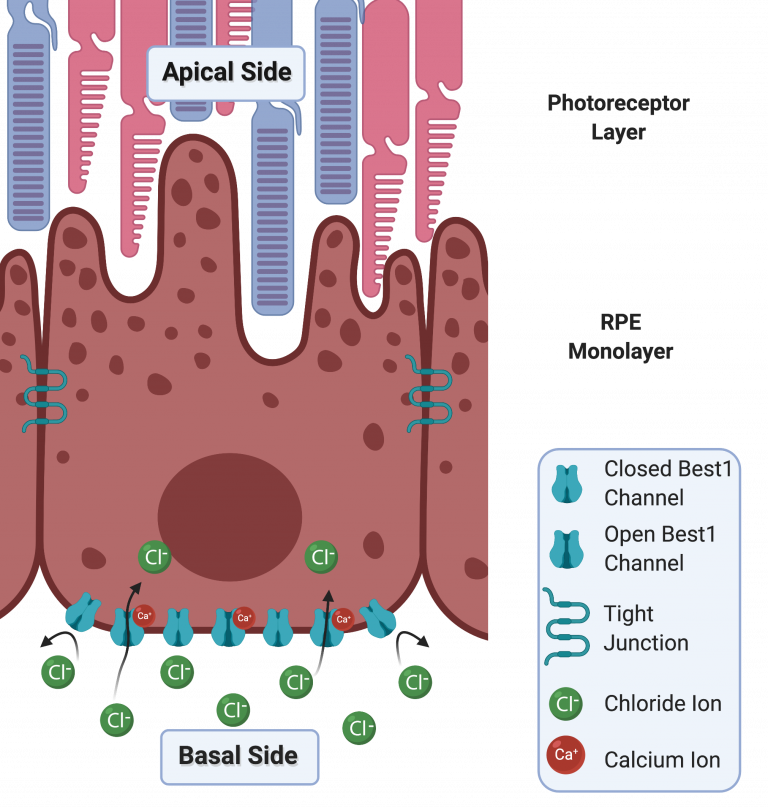
Research has shown that within RPE cells, the BEST1 protein may be involved in a number of processes, including the regulation and recruitment of calcium ions, the movement of other molecules within and into the RPE, and maintaining the normal shape of cells in certain conditions. BEST1 may also play a role in the normal development of the retina.
Away from the eye, research has shown that the protein may also act as a channel for molecules bigger than chloride ions and even be involved in neurotransmitter (chemical messengers used to convey signals in the central nervous system) release. This has led researchers to study how BEST1 works in the brain. Animal studies, involving mice, have also shown potential roles for BEST1 in the body outside of the eye and research is on-going to understand the complete picture of BEST1 function.
 Close
Close

