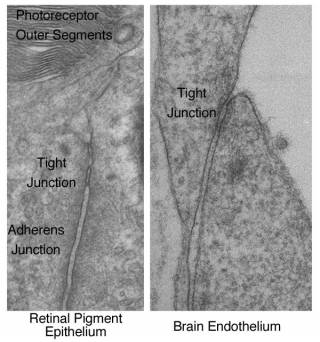
Morphology and Structure
- Tight junctions are intercellular adhesion complexes of epithelial and endothelial cells that form close membrane-membrane contacts
- Tight junctions are composed of an intricate protein network composed of transmembrane proteins and cytosolic proteins
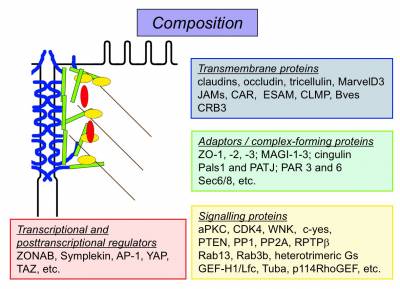
Functions
- Tight junctions form diffusion barriers between neighboring cells that regulate permeability across epithelia and endothelia
- Tight junctions support maintenance of cell surface polarity by forming an intramembrane diffusion barrier that restricts diffusion of lipids in the exoplasmic leaflet of the plasma membrane
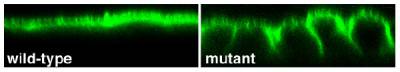
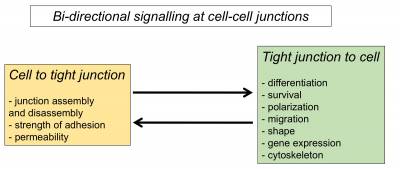
- Tight junctions regulate signalling pathways that control epithelial proliferation, differentiation and polarization
- Tight junctions form bidirectional signalling hubs that receive signals from the cells that regulate junctional functions and that transmit signals to the cells to guide cell behaviour and differentiation
Recent and key publications
Reviews
1. Zihni, C., et al., Tight junctions: from simple barriers to multifunctional molecular gates. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2016. 10.1038/nrm.2016.80;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27353478
2. Balda, M.S. and K. Matter, Tight junctions as regulators of tissue remodelling. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2016. 42: p. 94-101. 10.1016/j.ceb.2016.05.006;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27236618
3. Zihni, C., M.S. Balda, and K. Matter, Signalling at tight junctions during epithelial differentiation and microbial pathogenesis. J Cell Sci, 2014. 127(Pt 16): p. 3401-13. 10.1242/jcs.145029;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25125573
4. Matter, K. and M.S. Balda, SnapShot: Epithelial tight junctions. Cell, 2014. 157(4): p. 992-992 e1. 10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.027;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24813618
5. Balda, M.S. and K. Matter, Tight junctions in health and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2014. 36: p. 147-8. 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.11.001;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25454390
6. Terry, S., et al., Rho signaling and tight junction functions. Physiology (Bethesda), 2010. 25(1): p. 16-26. 10.1152/physiol.00034.2009;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20134025
7. Steed, E., M.S. Balda, and K. Matter, Dynamics and functions of tight junctions. Trends Cell Biol, 2010. 20(3): p. 142-9. 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.12.002;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20061152
Research papers
1. Zihni, C., et al., Tight junctions: from simple barriers to multifunctional molecular gates. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2016.
10.1038/nrm.2016.80;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27353478
2. Balda, M.S. and K. Matter, Tight junctions as regulators of tissue remodelling. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2016. 42: p. 94-101.
10.1016/j.ceb.2016.05.006;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27236618
3. Tornavaca, O., et al., ZO-1 controls endothelial adherens junctions, cell-cell tension, angiogenesis, and barrier formation. J Cell Biol, 2015. 208(6): p. 821-38.
10.1083/jcb.201404140; PMC4362456
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25753039
4. Zihni, C., M.S. Balda, and K. Matter, Signalling at tight junctions during epithelial differentiation and microbial pathogenesis. J Cell Sci, 2014. 127(Pt 16): p. 3401-13.
10.1242/jcs.145029;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25125573
5. Steed, E., et al., MarvelD3 couples tight junctions to the MEKK1-JNK pathway to regulate cell behavior and survival. J Cell Biol, 2014. 204(5): p. 821-38.
10.1083/jcb.201304115; PMC3941049
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24567356
6. Matter, K. and M.S. Balda, SnapShot: Epithelial tight junctions. Cell, 2014. 157(4): p. 992-992 e1.
10.1016/j.cell.2014.04.027;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24813618
7. Balda, M.S. and K. Matter, Tight junctions in health and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2014. 36: p. 147-8.
10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.11.001;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25454390
8. Nie, M., M.S. Balda, and K. Matter, Stress- and Rho-activated ZO-1-associated nucleic acid binding protein binding to p21 mRNA mediates stabilization, translation, and cell survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2012. 109(27): p. 10897-902.
10.1073/pnas.1118822109; PMC3390842
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22711822
9. Elbediwy, A., et al., Epithelial junction formation requires confinement of Cdc42 activity by a novel SH3BP1 complex. J Cell Biol, 2012. 198(4): p. 677-93.
10.1083/jcb.201202094; PMC3514035
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22891260
10. Terry, S.J., et al., Spatially restricted activation of RhoA signalling at epithelial junctions by p114RhoGEF drives junction formation and morphogenesis. Nat Cell Biol, 2011. 13(2): p. 159-66.
10.1038/ncb2156; PMC3032653
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21258369
11. Tsapara, A., et al., The RhoA activator GEF-H1/Lfc is a transforming growth factor-beta target gene and effector that regulates alpha-smooth muscle actin expression and cell migration. Mol Biol Cell, 2010. 21(6): p. 860-70.
10.1091/mbc.E09-07-0567; PMC2836967
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20089843
12. Terry, S., et al., Rho signaling and tight junction functions. Physiology (Bethesda), 2010. 25(1): p. 16-26.
10.1152/physiol.00034.2009;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20134025
13. Steed, E., M.S. Balda, and K. Matter, Dynamics and functions of tight junctions. Trends Cell Biol, 2010. 20(3): p. 142-9.
10.1016/j.tcb.2009.12.002;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20061152
14. Lima, W.R., et al., ZONAB promotes proliferation and represses differentiation of proximal tubule epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010. 21(3): p. 478-88.
10.1681/ASN.2009070698; PMC2831853
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20133480
15. Larre, I., et al., Ouabain modulates epithelial cell tight junction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010. 107(25): p. 11387-92.
10.1073/pnas.1000500107; PMC2895057
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20534449
16. Georgiadis, A., et al., The tight junction associated signalling proteins ZO-1 and ZONAB regulate retinal pigment epithelium homeostasis in mice. PLoS One, 2010. 5(12): p. e15730.
10.1371/journal.pone.0015730; PMC3012699
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21209887
17. Steed, E., et al., Identification of MarvelD3 as a tight junction-associated transmembrane protein of the occludin family. BMC Cell Biol, 2009. 10: p. 95.
10.1186/1471-2121-10-95; PMC2805614
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20028514
18. Nie, M., et al., The Y-box factor ZONAB/DbpA associates with GEF-H1/Lfc and mediates Rho-stimulated transcription. EMBO Rep, 2009. 10(10): p. 1125-31.
10.1038/embor.2009.182; PMC2738780
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19730435
19. Tsapara, A., K. Matter, and M.S. Balda, The heat-shock protein Apg-2 binds to the tight junction protein ZO-1 and regulates transcriptional activity of ZONAB. Mol Biol Cell, 2006. 17(3): p. 1322-30.
10.1091/mbc.E05-06-0507; PMC1382320
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16407410
20. Sourisseau, T., et al., Regulation of PCNA and cyclin D1 expression and epithelial morphogenesis by the ZO-1-regulated transcription factor ZONAB/DbpA. Mol Cell Biol, 2006. 26(6): p. 2387-98.
10.1128/MCB.26.6.2387-2398.2006; PMC1430269
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16508013
21. Kavanagh, E., et al., Functional interaction between the ZO-1-interacting transcription factor ZONAB/DbpA and the RNA processing factor symplekin. J Cell Sci, 2006. 119(Pt 24): p. 5098-105.
10.1242/jcs.03297;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17158914
22. Frankel, P., et al., RalA interacts with ZONAB in a cell density-dependent manner and regulates its transcriptional activity. EMBO J, 2005. 24(1): p. 54-62.
10.1038/sj.emboj.7600497; PMC544910
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15592429
23. Aijaz, S., et al., Binding of GEF-H1 to the tight junction-associated adaptor cingulin results in inhibition of Rho signaling and G1/S phase transition. Dev Cell, 2005. 8(5): p. 777-86.
10.1016/j.devcel.2005.03.003;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15866167
24. Benais-Pont, G., et al., Identification of a tight junction-associated guanine nucleotide exchange factor that activates Rho and regulates paracellular permeability. J Cell Biol, 2003. 160(5): p. 729-40.
10.1083/jcb.200211047; PMC2173357
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12604587
25. Balda, M.S., M.D. Garrett, and K. Matter, The ZO-1-associated Y-box factor ZONAB regulates epithelial cell proliferation and cell density. J Cell Biol, 2003. 160(3): p. 423-32.
10.1083/jcb.200210020; PMC2172662
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12566432
26. Huber, D., M.S. Balda, and K. Matter, Occludin modulates transepithelial migration of neutrophils. J Biol Chem, 2000. 275(8): p. 5773-8.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10681565
27. Balda, M.S., et al., Multiple domains of occludin are involved in the regulation of paracellular permeability. J Cell Biochem, 2000. 78(1): p. 85-96.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10797568
28. Balda, M.S. and K. Matter, The tight junction protein ZO-1 and an interacting transcription factor regulate ErbB-2 expression. EMBO J, 2000. 19(9): p. 2024-33.
10.1093/emboj/19.9.2024; PMC305688
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10790369
29. Matter, K. and M.S. Balda, Biogenesis of tight junctions: the C-terminal domain of occludin mediates basolateral targeting. J Cell Sci, 1998. 111 ( Pt 4): p. 511-9.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9443899
30. Balda, M.S., et al., Functional dissociation of paracellular permeability and transepithelial electrical resistance and disruption of the apical-basolateral intramembrane diffusion barrier by expression of a mutant tight junction membrane protein. J Cell Biol, 1996. 134(4): p. 1031-49.
PMC2120963
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8769425
31. Willott, E., et al., The tight junction protein ZO-1 is homologous to the Drosophila discs-large tumor suppressor protein of septate junctions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1993. 90(16): p. 7834-8.
PMC47237
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8395056
32. Balda, M.S., et al., Assembly of the tight junction: the role of diacylglycerol. J Cell Biol, 1993. 123(2): p. 293-302.
PMC2119828
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8408213
33. Balda, M.S. and J.M. Anderson, Two classes of tight junctions are revealed by ZO-1 isoforms. Am J Physiol, 1993. 264(4 Pt 1): p. C918-24.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7682777
34. Balda, M.S., et al., Assembly and sealing of tight junctions: possible participation of G-proteins, phospholipase C, protein kinase C and calmodulin. J Membr Biol, 1991. 122(3): p. 193-202.
 Close
Close

