Resilience of integrated school and road system using combined Agent-based and Bayesian network
Exposure of school infrastructure to multi-hazards poses significant risk to vulnerable populations of students and their education process.

20 May 2022
Exposure of school infrastructure to multi-hazards poses significant risk to vulnerable populations of students and their education process. This project under the UNESCO Chair involves the development of a multi-hazard multi-criteria framework for resilience modelling of school infrastructure systems. The project proposes to develop a probabilistic framework, combining the Agent-based (AB) and Bayesian network (BN) approaches for system disruption and resilience analysis.
An integrated Agent-based and Bayesian network model (AB-BN) is being developed and employed to track the time-varying functionality of the integrated school-road networks, under damaging earthquakes and floods.
Motivation
Exposure of school infrastructure and associated road network to natural hazards results in significant risk to vulnerable populations of students and their education process. With increasing imbalance in the environmental systems due to rapid urbanisation and climate change, disruption from flood and earthquake hazards to school education systems in the most vulnerable geographic locations is a growing concern. Hence, holistic resilience frameworks accounting for physical, functional and social elements of post-disaster education continuity is the need of the hour.
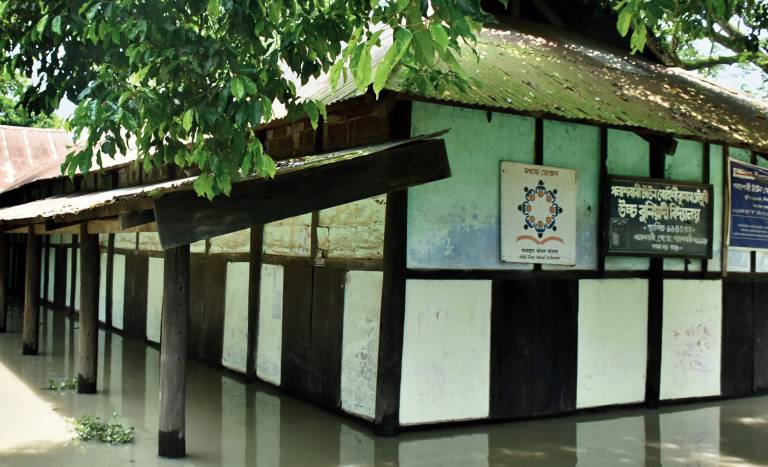

A school submerged in floodwater, India (Telegraph India, Nov 2019)
Objective
The AB-BN framework aims to estimate the disruption to education due to multiple hazards to quantify its resilience, considering physical, functional and social vulnerability aspects of the infrastructure, as illustrated, and explores the mobility between the schools by the performance of integrated road network.

Case studies of school-road systems
- Cagayan de Oro, Philippines
- Dominican Republic
The project is planned in consultation and close collaboration with the local universities, governments, and decision-makers in order to understand their specific inputs and requirements with respect to education continuity after natural hazards at regional scale, and co-design mitigation strategies, which would inform the development of finer details of the resilience framework outlined.
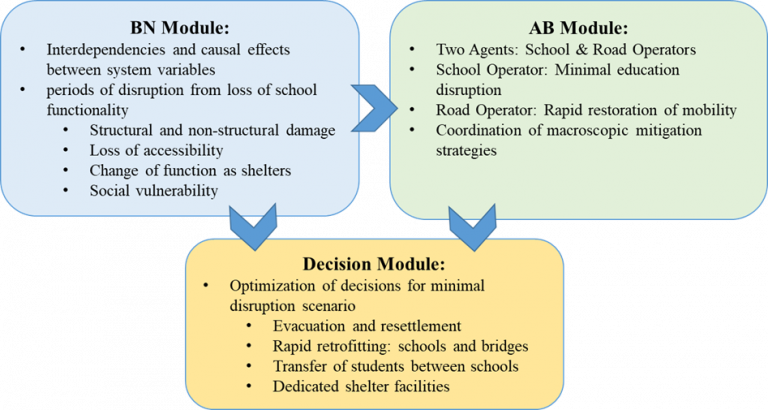
Outcomes
The resulting AB-BN Model would:
- Provide a complete probabilistic representation of the system
- Quantify resilience of the system
- Allow scenario-based assessment
- Quantify the influence of different policy decisions and intervention strategies
- Assist the authorities with decision-making.
Research Team
- Professor Dina D’Ayala
- Dr. Li Sun
- Dr. Ahsana Parammal Vatteri
Research Partners
- Xavier University: Dr Dexter Lo, Dr. Anabel Abuzo
- UNESCO Regional Office: Dominican Republic
Funding
- UNESCO Chair on Disaster Risk Reduction and Resilience Engineering, UCL.
 Close
Close

