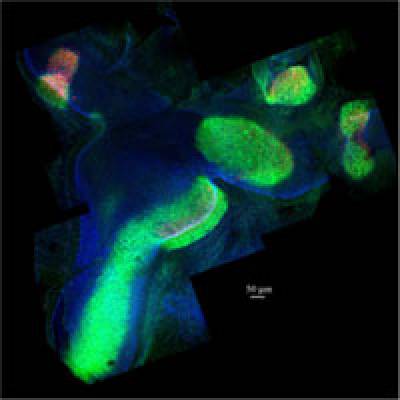
- The functions of notch signalling during inner ear development and regeneration
-
Notch signalling is one of the most important cell-to-cell communication pathways during inner ear development and regeneration. We are developing and using live-imaging and genetic tricks in chicken embryos to understand the functions of Notch in i) establishing the early/prosensory domains of the inner ear and ii) the regulation of hair cell versus supporting cell fate decisions.
Collaborators: J. Gale (Ear Institute), J. Stone (U. Seattle, USA), K. Steel (Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute), B. Alsina (U. Pompeu Fabra, Spain)
- Eddison, M; Weber, SJ; Ariza-McNaughton, L; Lewis, J; Daudet, N; (2015) Numb is not a critical regulator of Notch-mediated cell fate decisions in the developing chick inner ear. Front Cell Neurosci , 9 , Article 74. 10.3389/fncel.2015.00074.
- Chrysostomou, E., Gale, J.E., Daudet, N. (2012). Delta-like 1 and lateral inhibition during hair cell formation in the chicken inner ear: evidence against cis-inhibition.. Development (Cambridge), 139 (20), 3764-3774. doi:10.1242/dev.074476
- Bird, J.E., Daudet, N., Warchol, M.E., Gale, J.E. (2010). Supporting cells eliminate dying sensory hair cells to maintain epithelial integrity in the avian inner ear.. J NEUROSCI, 30 (37), 12545-12556. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3042-10.2010
- Daudet, N., Gibson, R., Shang, J., Bernard, A., Lewis, J., Stone, J. (2009). Notch regulation of progenitor cell behaviour in quiescent and regenerating auditory epithelium of mature birds.. DEV BIOL, 326 (1), 86-100. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.10.033
- Daudet, N., Ariza-McNaughton, L., Lewis, J. (2007). Notch signalling is needed to maintain, but not to initiate, the formation of prosensory patches in the chick inner ear. DEVELOPMENT, 134 (12), 2369-2378. doi:10.1242/dev.001842
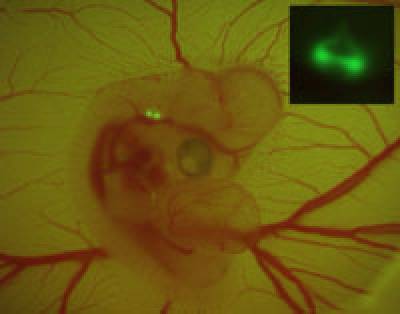
- Transcriptional networks in the control of hair cell differentiation
-
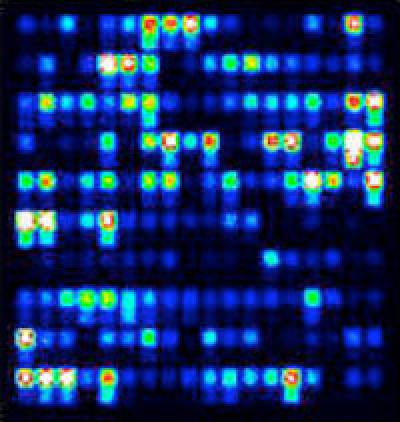
We are using transcriptome analysis and functional approaches in vivo and in vitro to get new insights into the genetic networks regulated by Notch signalling during ear development. We are also interested in the specific roles of the SoxB and bHLH transcription factors in the control of hair cell formation and regeneration, and we are using this knowledge to improve the existing methods for hair cell generation via genetic reprogramming.
Collaborators: V. Plagnol (UCL); D. Henrique (University of Lisboa, Portugal)
- Freeman, S.D., Daudet, N. (2012). Artificial induction of Sox21 regulates sensory cell formation in the embryonic chicken inner ear.. PLOS ONE, 7 (10), doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046387
- Costa, A., Sanchez-Guardado, L., Juniat, S., Gale, J.E., Daudet, N., Henrique, D. (2015). Generation of sensory hair cells by genetic programming with a combination of transcription factors. Development (Cambridge), 142 (11), 1948-1959. doi:10.1242/dev.119149
- Stereocilia formation and maintenance
-
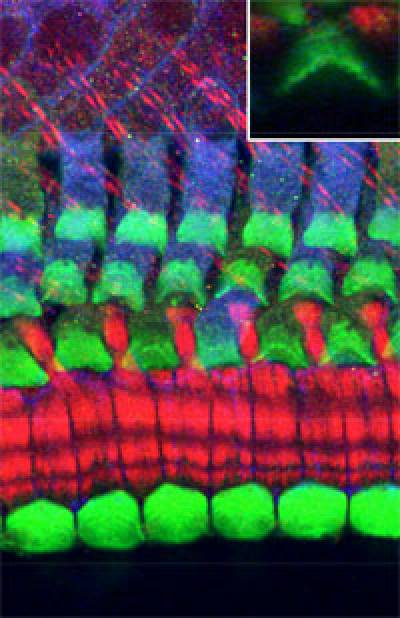
Stereocilia are microvilli-like structures arranged into a neat bundle at the surface of each hair cell. When fluid movements occur in the liquid-filled compartments of the inner ear, stereocilia are displaced, triggering the release of neurotransmitters by hair cells. Mutations in genes encoding molecular components of stereocilia are frequently associated to hereditary forms of deafness. Our work has uncovered a specific function for an actin-bundling protein named Plastin1 (also known as Fimbrin) in the maintenance of auditory hair cell stereocilia, and we are also looking at the signalling pathways that regulate the assembly of the stereociliary bundles during embryonic development.
Collaborators: A. Bullen, A. Forge, R. Taylor (Ear Institute), F. Rivero (U. of Hull), S. Johnson, W. Marcotti (U. of Sheffield), M. Davey (University of Edinburgh)
- Taylor, R., Bullen, A., Johnson, S.L., Grimm-Günter, E.M., Rivero, F., Marcotti, W., ...Daudet, N. (2015). Absence of plastin 1 causes abnormal maintenance of hair cell stereocilia and a moderate form of hearing loss in mice.. Human Molecular Genetics, 24 (1), 37-49. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddu417
- Stephen, L.A., Tawamie, H., Davis, G.M., Tebbe, L., Nürnberg, P., Nürnberg, G., ...Uebe, S. (2015). TALPID3 controls centrosome and cell polarity and the human ortholog KIAA0586 is mutated in Joubert syndrome ( JBTS23 ). eLife, 4 doi:10.7554/eLife.08077
 Close
Close