The wealth of data collected since the study began has allowed us to examine the interrelationships between socio-economic, biological, psychosocial, and behavioural factors.
By combining existing 35 years of data on environmental exposures (social, behavioural, cardiometabolic, inflammatory) and chronic disease with repeat assessment of cognitive and motor function (6 measures from 1997 to 2023) Whitehall II is uniquely positioned internationally to disability and dementia.
Current Research on Ageing
Ageing is not characterised by universal decline. Rather, variations in the speed of ageing result in people of the same age becoming increasingly dissimilar in terms of cognitive capability, mental and physical health and functioning over time.
Understanding the causes of this age-related individual heterogeneity and its distribution by social group is the core focus of our current work.
In addition to providing insights into individual and social differences in the development of frailty, disability, dependence, and dementia, our work enables the determination of optimal time windows and targets for interventions that maximize the potential for healthy-ageing and independent living.
Our recent research highlights are:
- Generalizability of Whitehall II findings
As Whitehall II is an occupational cohort study, prevalence of risk factors and incidence of disease are lower than the general population. Nevertheless, the associations between causal risk factors and disease in Whitehall II are similar to those in the population-based British Regional Heart Study (Batty et al, Epidemiology 2014).
Whitehall II has contributed to >100 research consortia papers and the results have been consistent with summary estimates from other studies. Thus, the causal risk factor-health outcome associations observed in Whitehall II are very likely to be generalizable, applicable to the UK and other developed countries.
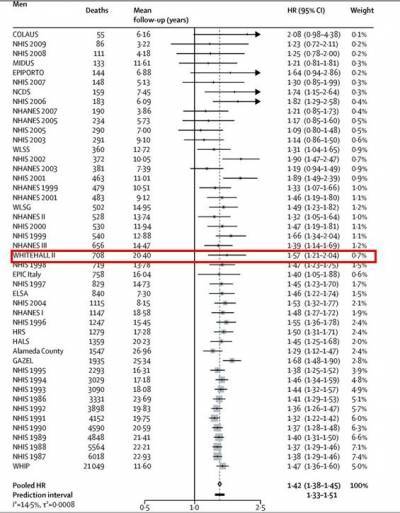
See for example how Whitehall II results compare to other studies in the graph below, which shows the inverse association between socioeconomic status and mortality in Whitehall II and 45 other cohort studies from Europe, the US and Asia (Stringhini et al. Lancet 2017)
- Cognitive Ageing and Dementia
The unique feature of the Whitehall II cognitive data is assessment starting at age 45, allowing us to study the social, behavioural and biological determinants of heterogeneity in cognitive decline, starting in midlife and dementia.
- Association of sleep duration at age 50, 60, and 70 years with risk of multimorbidity in the UK: 25-year follow-up of the Whitehall II cohort study. Sabia S, Dugravot A, Léger D, Ben Hassen C, Kivimaki M, Singh-Manoux A. PLoS Med. 2022;19(10):e1004109.
- Association between age at onset of multimorbidity and incidence of dementia: 30 year follow-up in Whitehall II prospective cohort study. Ben Hassen C, Fayosse A, Landré B, Raggi M, Bloomberg M, Sabia S, Singh-Manoux A. BMJ. 2022;376:e068005.
- Immune system-wide Mendelian randomization and triangulation analyses support autoimmunity as a modifiable component in dementia-causing diseases. Lindbohm JV, Mars N, Sipilä PN, et al. Nat Aging. 2022;2:956–972.
- Cognitive stimulation in the workplace, plasma proteins, and risk of dementia: three analyses of population cohort studies. Kivimäki M, Walker KA, Pentti J, et al. BMJ. 2021;374:n1804.
- Association of midlife diet with subsequent risk for dementia. Akbaraly TN, Singh-Manoux A, Dugravot A, Brunner EJ, Kivimäki M, Sabia S. JAMA. 2019;321:957-968.
- Association between systolic blood pressure and dementia in the Whitehall II cohort study: role of age, duration, and threshold used to define hypertension. Abell JG, Kivimäki M, Dugravot A, Tabak AG, Fayosse A, Shipley M, Sabia S, Singh-Manoux A. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(33):3119-3125
- Moderate alcohol consumption as risk factor for adverse brain outcomes and cognitive decline: longitudinal cohort study. Topiwala A, Allan CL, Valkanova V, Zsoldos E, Filippini N, Sexton C, Mahmood A, Fooks P, Singh-Manoux A, Mackay CE, Kivimäki M, Ebmeier KP. BMJ. 2017;357:j2353.
- Trajectories of Depressive Symptoms Before Diagnosis of Dementia: A 28-Year Follow-up Study. Singh-Manoux A, Dugravot A, Fournier A, Abell J, Ebmeier K, Kivimäki M, Sabia S. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(7):712-718. Atrial fibrillation as a risk factor for cognitive decline and dementia. Singh-Manoux A, Fayosse A, Sabia S, Canonico M, Bobak M, Elbaz A, Kivimäki M, Dugravot A. Eur Heart J. 2017;38(34):2612-2618.
- Midlife type 2 diabetes and poor glycaemic control as risk factors for cognitive decline in early old age: a post-hoc analysis of the Whitehall II cohort study. Tuligenga RH, Dugravot A, Tabák AG, Elbaz A, Brunner EJ, Kivimäki M, Singh-Manoux A. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:228-35.
- Midlife stroke risk and cognitive decline: a 10-year follow-up of the Whitehall II cohort study. Kaffashian S, Dugravot A, Brunner EJ, Sabia S, Ankri J, Kivimäki M, Singh-Manoux A. Alzheimers Dement. 2013;9:572-9.
- Impact of smoking on cognitive decline in early old age: the Whitehall II cohort study. Sabia S, Elbaz A, Dugravot A, Head J, Shipley M, Hagger-Johnson G, Kivimaki M, Singh-Manoux A. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69:627-35.
- Timing of onset of cognitive decline: results from Whitehall II prospective cohort study. Singh-Manoux A, Kivimaki M, Glymour MM, Elbaz A, Berr C, Ebmeier KP, Ferrie JE, Dugravot A. BMJ. 2012;344:d7622.
- Does cognitive reserve shape cognitive decline? Singh-Manoux A, Marmot MG, Glymour M, Sabia S, Kivimäki M, Dugravot A. Ann Neurol. 2011;70:296-304.
- Cardiometabolic Health
Whitehall II has collected an unrivalled set of multiple repeat measures over 30 years of follow-up, complementing our cardiovascular morbidity and mortality follow-up. For example, blood pressure and body mass index have been measured on 7 occasions and oral glucose tolerance on 4 occasions. Our longitudinal studies of diabetes development have attracted much attention.
The causes and consequences of aortic stiffening is a novel focus of our cardiometabolic research, which is also relevant to those interested in interventions to reduce vascular ageing. Whitehall II has now collected three measures of carotid-femoral pulse wave velocity.
- The multiple roles of life stress in metabolic disorders. Kivimäki M, Bartolomucci A, Kawachi I. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19(1):10-27.
- Risk of Macrovascular and Microvascular Disease in Diabetes Diagnosed Using Oral Glucose Tolerance Test With and Without Confirmation by Hemoglobin A1c: The Whitehall II Cohort Study. Tabák AG, Brunner EJ, Lindbohm JV, Singh-Manoux A, Shipley MJ, Sattar N, Kivimäki M. Circulation. 2022;146(13):995-1005.
- Metabolomic profiles predict individual multidisease outcomes. Buergel T, Steinfeldt J, Ruyoga G, et al. Nat Med. 2022;28(11):2309-2320.
- Five-year versus risk-category-specific screening intervals for cardiovascular disease prevention: a cohort study. Lindbohm JV, Sipilä PN, Mars NJ, Pentti J, Ahmadi-Abhari S, Brunner EJ, Shipley MJ, Singh-Manoux A, Tabak A, Kivimaki M. Lancet Public Health 2019;4:e189-e199.
- Global, regional, and country-specific lifetime risks of stroke, 1990 and 2016. Feigin V, GBD 2016 Lifetime Risk of Stroke Collaborators. N Engl J Med 2018;379:2429-37.
- Obesity and loss of disease-free years owing to major non-communicable diseases: a multicohort study. Nyberg ST, Batty GD, Pentti J, Virtanen M, Alfredsson L, Fransson EI, Goldberg M, Heikkilä K, Jokela M, Knutsson A, Koskenvuo M, Lallukka T, Leineweber E, Lindbohm JV, Madsen IEH, Magnusson Hanson LL, Nordin M, Oksanen T, Pietiläinen O, Rahkonen O, Rugulies R, Shipley MJ, Stenholm S, Suominen S, Theorell T, Vahtera J, Westerholm PJM, Westerlund H, Zins M, Hamer M, Singh-Manoux A, Bell JA, Ferrie JE, Kivimaki M. Lancet Public Health 2018;3:e490-7.
- Overweight, obesity and risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity: Pooled analysis of individual-level data on 120,813 adults from 16 cohort studies in high-income countries. Kivimaki M et al. Lancet Public Health 2017;2:e277-e285.
- Incidence of Metabolic Risk Factors Among Healthy Obese Adults: 20-Year Follow-Up. Bell JA, Hamer M, Batty GD, Singh-Manoux A, Sabia S, Kivimäki M. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015 Aug 18;66(7):871-3.
- The natural course of healthy obesity over 20 years. Bell JA, Hamer M, Sabia S, Singh-Manoux A, Batty GD, Kivimaki M. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2015 Jan 6;65(1):101-2.
- Adiposity, Obesity, and Arterial Aging: Longitudinal Study of Aortic Stiffness in the Whitehall II Cohort. Brunner EJ, Shipley MJ, Ahmadi-Abhari S, Tabak AG, McEniery CM, Wilkinson IB, Marmot MG, Singh-Manoux A, Kivimaki M. Hypertension. 2015; 66(2): 294-300.
- Prediabetes: a high-risk state for diabetes development. Tabák AG, Herder C, Rathmann W, Brunner EJ, Kivimäki M. Lancet. 2012;379: 2279-90.
- Physical activity and inflammatory markers over 10 years: follow-up in men and women from the Whitehall II cohort study. Hamer M, Sabia S, Batty GD, Shipley MJ, Tabák AG, Singh-Manoux A, Kivimaki M. Circulation. 2012; 126: 928-33.
- Arterial stiffness, physical function, and functional limitation: the Whitehall II Study. Brunner EJ, Shipley MJ, Witte DR, Singh-Manoux A, Britton AR, Tabak AG, McEniery CM, Wilkinson IB, Kivimaki M. Hypertension. 2011; 57: 1003-9.
- Association of diurnal patterns in salivary cortisol with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: findings from the Whitehall II study. Kumari M, Shipley M, Stafford M, Kivimaki M. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011; 96: 1478-85.
- Trajectories of glycaemia, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion before diagnosis of type 2 diabetes: an analysis from the Whitehall II study. Tabák AG, Jokela M, Akbaraly TN, Brunner EJ, Kivimäki M, Witte DR. Lancet. 2009; 373: 2215-21.
- Physical Functioning and Mental Health
A major aim of our research is to identify midlife risk factors and protective factors for old-age functional limitations and depression. In addition to social circumstances, lifestyle and chronic diseases, we examine the role of biological factors, such as low-grade inflammation, in predicting functioning and mental well-being at older ages.
- Trajectories of physical and mental functioning over 25 years before onset of frailty: results from the Whitehall II cohort study. Landré B, Ben Hassen C, Kivimaki M, Bloomberg M, Dugravot A, Schniztler A, Sabia S, Singh-Manoux A. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2023;14(1):288-297.
- Association of Major Surgical Admissions With Quality of Life: 19-Year Follow-up of the Whitehall II Longitudinal Prospective Cohort Study. Krause BM, Manning HJ, Sabia S, Singh-Manoux A, Sanders RD. JAMA Surg. 2022;157(3):275-277.
- Terminal decline in objective and self-reported measures of motor function before death: 10 year follow-up of Whitehall II cohort study. Landré B, Fayosse A, Ben Hassen C, Machado-Fragua MD, Dumurgier J, Kivimaki M, Sabia S, Singh-Manoux A. BMJ. 2021;374:n1743.
- Association of sleep with cognitive function during retirement transition: the Whitehall II study. Teräs T, Rovio S, Pentti J, Head J, Kivimäki M, Stenholm S. Sleep. 2023;46(1):zsac237.
- Healthy obesity and risk of accelerated functional decline and disability. Bell JA, Sabia S, Singh-Manoux A, Hamer M, Kivimäki M. Int J Obes (Lond). 2017;41(6):866-872.
- Midlife Risk Factors for Impaired Physical and Cognitive Functioning at Older Ages: A Cohort Study. Brunner EJ, Welch CA, Shipley MJ, Ahmadi-Abhari S, Singh-Manoux A, Kivimäki M. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017;72(2):237-242
- Trajectories of Unhealthy Behaviors in Midlife and Risk of Disability at Older Ages in the Whitehall II Cohort Study. Artaud F, Sabia S, Dugravot A, Kivimaki M, Singh-Manoux A, Elbaz A. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016;71(11):1500-1506.
- Long-term inflammation increases risk of common mental disorder: a cohort study. Kivimäki M, Shipley MJ, Batty GD, Hamer M, Akbaraly TN, Kumari M, Jokela M, Virtanen M, Lowe GD, Ebmeier KP, Brunner EJ, Singh-Manoux A. Mol Psychiatry. 2014; 19: 149-50.
- Association of metabolically healthy obesity with depressive symptoms: pooled analysis of eight studies. Jokela M, Hamer M, Singh-Manoux A, Batty GD, Kivimäki M. Mol Psychiatry. 2014;19:910-4.
- Depression and type 2 diabetes: a causal association? Tabák AG, Akbaraly TN, Batty GD, Kivimäki M. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:236-45.
- Trajectories of the Framingham general cardiovascular risk profile in midlife and poor motor function later in life: the Whitehall II study. Elbaz A, Shipley MJ, Nabi H, Brunner EJ, Kivimaki M, Singh-Manoux A. Int J Cardiol. 2014;172: 96-102.
- Cumulative associations between midlife health behaviors and physical functioning in early old age: a 17-year prospective cohort study. Sabia S, Elbaz A, Rouveau N, Brunner EJ, Kivimaki M, Singh-Manoux A. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2014;62:1860-8.
- Vascular risk status as a predictor of later-life depressive symptoms: a cohort study. Kivimäki M, Shipley MJ, Allan CL, Sexton CE, Jokela M, Virtanen M, Tiemeier H, Ebmeier KP, Singh-Manoux A. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;72:324-30.
- Common mental disorder and obesity: insight from four repeat measures over 19 years: prospective Whitehall II cohort study. Kivimäki M, Lawlor DA, Singh-Manoux A, Batty GD, Ferrie JE, Shipley MJ, Nabi H, Sabia S, Marmot MG, Jokela M. BMJ. 2009;339:b3765.
- Socioeconomic and occupational stressors
Biological, environmental and lifestyle factors explaining differences in health between people from different socioeconomic circumstances have been a key research area for Whitehall II since the beginning of the study. Our findings have had a strong impact on health policy nationally and internationally. To understand the health effects of workplace factors, such as work stress, we have combined data from Whitehall II to those from other cohort studies.
- The multiple roles of life stress in metabolic disorders. Kivimäki M, Bartolomucci A, Kawachi I. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2023;19(1):10-27.
- Contribution of smoking towards the association between socioeconomic position and dementia: 32-year follow-up of the Whitehall II prospective cohort study. Raggi M, Dugravot A, Valeri L, Machado-Fragua MD, Dumurgier J, Kivimaki M, Sabia S, Singh-Manoux A. Lancet Reg Health Eur. 2022;23:100516.
- Sex differences in functional limitations and the role of socioeconomic factors: a multi-cohort analysis. Bloomberg M, Dugravot A, Landré B, Britton A, Steptoe A, Singh-Manoux A, Sabia S. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021;2(12):e780-e790.
- Sex differences and the role of education in cognitive ageing: analysis of two UK-based prospective cohort studies. Bloomberg M, Dugravot A, Dumurgier J, Kivimaki M, Fayosse A, Steptoe A, Britton A, Singh-Manoux A, Sabia S. Lancet Public Health. 2021;6(2):e106-e115.
- Association between socioeconomic status and the development of mental and physical health conditions in adulthood: a multi-cohort study. Kivimäki M, Batty GD, Pentti J, Shipley MJ, Sipilä PN, Nyberg ST, Suominen SB, Oksanen T, Stenholm S, Virtanen M, Marmot MG, Singh-Manoux A, Brunner EJ, Lindbohm JV, Ferrie JE, Vahtera J. Lancet Public Health. 2020;5(3):e140-e149.
- Clinical, socioeconomic and behavioural factors at age 50 and risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity and mortality: a cohort study. Singh-Manoux A, Fayosse A, Sabia S, Tabak A, Shipley M, Dugravot A, Kivimaki M. PLoS Med 2018;15(5):e1002571.
- Midlife contributors to socioeconomic differences in later life frailty: prospective study. Brunner EJ, Shipley MJ, Ahmadi-Abhari S, Valencia Hernandez C, Abell JG, Singh-Manoux A, Kawachi I, Kivimaki M. Lancet Public Health 2018;3:e313-e322.
- Effects of stress on the development and progression of cardiovascular disease. Kivimaki M, Steptoe A. Nature Reviews Cardiology 2018;15:215-229.
- Work stress and risk of death in men and women with and without cardiometabolic disease: a multicohort study. Kivimaki M et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2018;6:705-713.
- Socioeconomic status and the 25 × 25 risk factors as determinants of premature mortality: a multicohort study and meta-analysis of 1·7 million men and women. Stringhini S, Carmeli C, Jokela M, Avendaño M, Muennig P, Guida F, Ricceri F, d'Errico A, Barros H, Bochud M, Chadeau-Hyam M, Clavel-Chapelon F, Costa G, Delpierre C, Fraga S, Goldberg M, Giles GG, Krogh V, Kelly-Irving M, Layte R, Lasserre AM, Marmot MG, Preisig M, Shipley MJ, Vollenweider P, Zins M, Kawachi I, Steptoe A, Mackenbach JP, Vineis P, Kivimäki M; LIFEPATH consortium. Lancet. 2017 Mar 25;389(10075):1229-1237
- Long working hours and risk of coronary heart disease and stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published and unpublished data for 603,838 individuals. Kivimäki M, Jokela M, Nyberg ST, Singh-Manoux A, Fransson EI, Alfredsson L, Bjorner JB, Borritz M, Burr H, Casini A, Clays E, De Bacquer D, Dragano N, Erbel R, Geuskens GA, Hamer M, Hooftman WE, Houtman IL, Jöckel KH, Kittel F, Knutsson A, Koskenvuo M, Lunau T, Madsen IE, Nielsen ML, Nordin M, Oksanen T, Pejtersen JH, Pentti J, Rugulies R, Salo P, Shipley MJ, Siegrist J, Steptoe A, Suominen SB, Theorell T, Vahtera J, Westerholm PJ, Westerlund H, O'Reilly D, Kumari M, Batty GD, Ferrie JE, Virtanen M; IPD-Work Consortium. Lancet. 2015 Oct 31;386(10005):1739-46.
- Association of lifecourse socioeconomic status with chronic inflammation and type 2 diabetes risk: the Whitehall II prospective cohort study. Stringhini S, Batty GD, Bovet P, Shipley MJ, Marmot MG, Kumari M, Tabak AG, Kivimäki M. PLoS Med. 2013; 10: e1001479.
- Job strain as a risk factor for coronary heart disease: a collaborative meta-analysis of individual participant data. Kivimäki M, Nyberg ST, Batty GD, Fransson EI, Heikkilä K, Alfredsson L, Bjorner JB, Borritz M, Burr H, Casini A, Clays E, De Bacquer D, Dragano N, Ferrie JE, Geuskens GA, Goldberg M, Hamer M, Hooftman WE, Houtman IL, Joensuu M, Jokela M, Kittel F, Knutsson A, Koskenvuo M, Koskinen A, Kouvonen A, Kumari M, Madsen IE, Marmot MG, Nielsen ML, Nordin M, Oksanen T, Pentti J, Rugulies R, Salo P, Siegrist J, Singh-Manoux A, Suominen SB, Väänänen A, Vahtera J, Virtanen M, Westerholm PJ, Westerlund H, Zins M, Steptoe A, Theorell T; IPD-Work Consortium. Lancet. 2012; 380: 1491-7.
- Contribution of modifiable risk factors to social inequalities in type 2 diabetes: prospective Whitehall II cohort study. Stringhini S, Tabak AG, Akbaraly TN, Sabia S, Shipley MJ, Marmot MG, Brunner EJ, Batty GD, Bovet P, Kivimäki M. BMJ. 2012; 345: e5452.
- Association of socioeconomic position with health behaviors and mortality. Stringhini S, Sabia S, Shipley M, Brunner E, Nabi H, Kivimaki M, Singh-Manoux A. JAMA. 2010; 303: 1159-66.
 Close
Close

