Bacterium's coiled anchor causes urinary tract infections
12 January 2016
UCL and Birkbeck-led research reveals the flexible, coiled structure used by bacteria to anchor onto the lining of the urinary tract, which allows them to thrive and cause infections.
 Understanding this structure in atomic detail will help the development of new drugs
to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs), say the scientists behind the study.
Understanding this structure in atomic detail will help the development of new drugs
to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs), say the scientists behind the study.
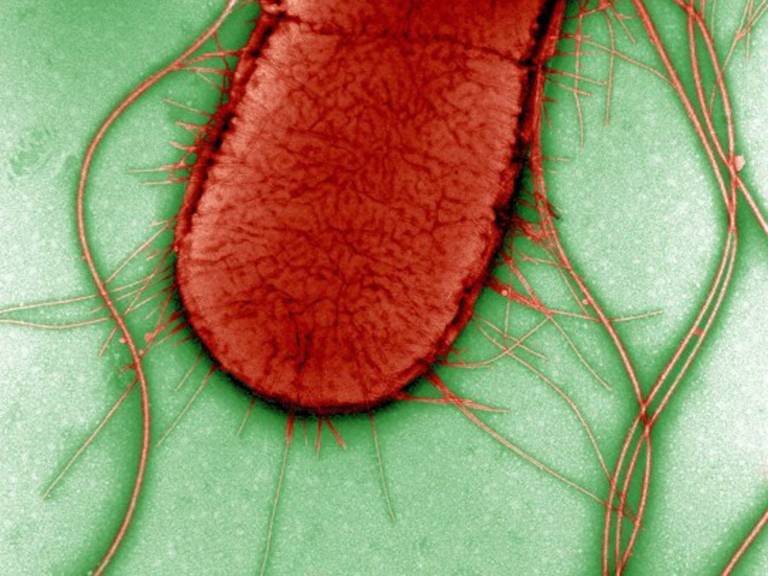
The bacterium, a form of E. coli, is responsible for up to 90 percent of urinary tract infections. It grips the urinary tract lining with tiny appendages, known as pili, which are coiled tightly like a spring. When urine flows, the coiled pili flex and bend like a telephone cord, allowing the bacteria to survive the large forces without breaking.
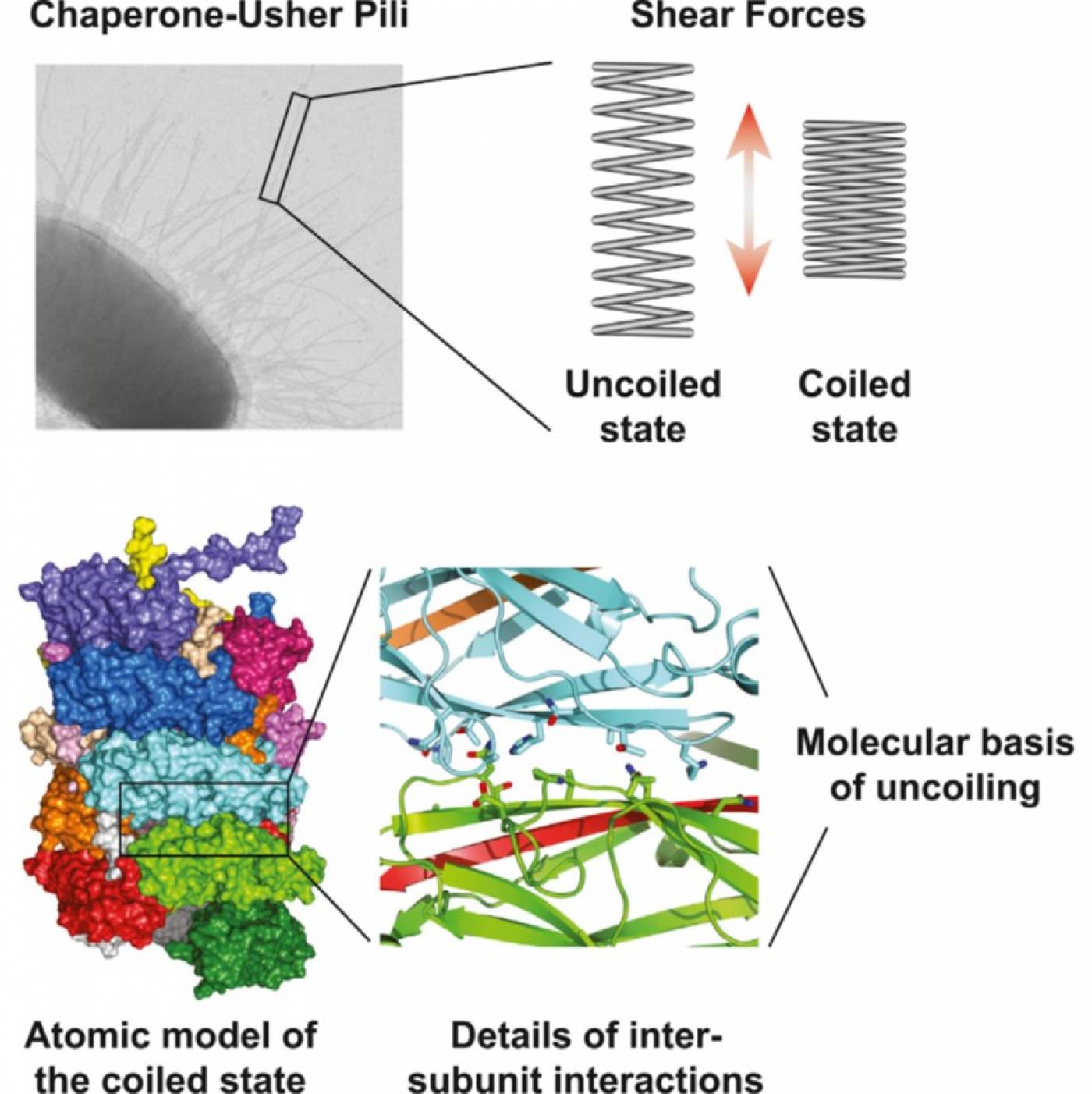
For the study, published in Cell, Professor Gabriel Waksman (UCL/Birkbeck Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology) and his colleagues collaborated with Professor Ed Egelman (University of Virginia School of Medicine) to produce the most detailed depiction of the pili ever assembled. UCL and Birkbeck researchers performed submicroscopic imaging using a powerful electron microscope at Diamond Light Source, the results of which were assembled by Professor Egelman into a colourful portrait that has been impossible to create until now.
"These pili are important surface-exposed appendages that bacteria use to recognize and adhere to host tissues. They are also important in making bacterial biofilms, which form on teeth and gums, or on the surface of cardiac devices or ships," said Professor Waksman.
"The main challenge is that, until recently, there was no method to determine the atomic-resolution details of these appendages. However, recently, revolutionary progress in electron microscopy has changed that. We can now generate views of these pili at very high resolution, yielding unprecedented atomic details that shed light into the function of these pili."
Understanding the shape and structure of the pili is a key step toward producing ways to block the bacteria from producing the common and often painful infections. It's estimated that up to half of women develop a UTI during their lifetime but using this information, drugs could be developed which prevent the pili from attaching to the urinary tract.
"These pili are absolutely essential for the infectivity, because it's the pili that attach very strongly to the lining of the urinary tract," Professor Egelman noted. "If these pili aren't assembled, then these bugs aren't infective at all. They'd wash right out."
Source
- University of Virginia School of Medicine
Images
- Electron micrograph of E. coli (courtesy of Wellcome Trust via Flickr)
- An atomic model of the P pilus rod (courtesy of Professor Gabriel Waksman, UCL/Birkbeck)
 Close
Close

