Further dental analysis of Homo antecessor suggests it was basal to Homo sapiens, Homo neanderthalensis and the Denisovan Hominins
24 January 2019
Here we analyze the unpublished hominin dental remains recovered from the late Early Pleistocene Gran Dolina-TD6.
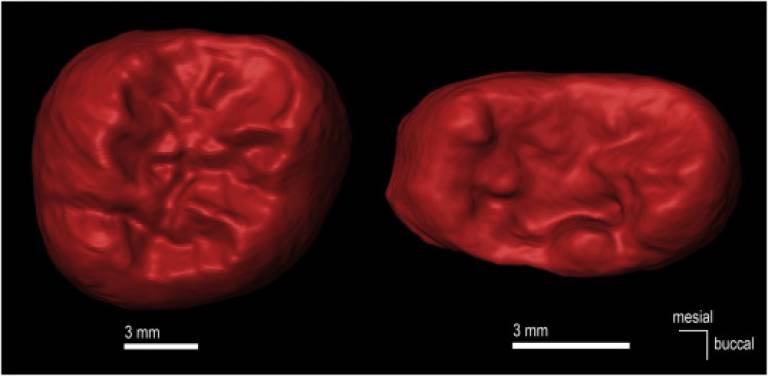 2 level of the Sierra de Atapuerca (northern Spain), as well as provide a reassessment of the whole TD6.2 hominin dental sample. Comparative descriptions of the outer enamel surface (OES) and the enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) are provided. Overall, the data presented here support the taxonomic validity of Homo antecessor, since this species presents a unique mosaic of traits. Homo antecessor displays several primitive features for the genus Homo as well as some traits exclusively shared with Early and Middle Pleistocene Eurasian hominins. Some of these Eurasian traits were retained by the Middle Pleistocene hominins of Europe, and subsequently became the typical condition of the Neanderthal lineage. Although other skeletal parts present resemblances with Homo sapiens, TD6.2 teeth do not show any synapomorphy with modern humans. In addition, TD6.2 teeth can be well differentiated from those of Asian Homo erectus. The dental evidence is compatible with previous hypothesis about H. antecessor belonging to the basal population from which H. sapiens, Homo neanderthalensis, and Denisovans emerged. Future findings and additional research may help to elucidate the precise phylogenetic link among them.
2 level of the Sierra de Atapuerca (northern Spain), as well as provide a reassessment of the whole TD6.2 hominin dental sample. Comparative descriptions of the outer enamel surface (OES) and the enamel-dentine junction (EDJ) are provided. Overall, the data presented here support the taxonomic validity of Homo antecessor, since this species presents a unique mosaic of traits. Homo antecessor displays several primitive features for the genus Homo as well as some traits exclusively shared with Early and Middle Pleistocene Eurasian hominins. Some of these Eurasian traits were retained by the Middle Pleistocene hominins of Europe, and subsequently became the typical condition of the Neanderthal lineage. Although other skeletal parts present resemblances with Homo sapiens, TD6.2 teeth do not show any synapomorphy with modern humans. In addition, TD6.2 teeth can be well differentiated from those of Asian Homo erectus. The dental evidence is compatible with previous hypothesis about H. antecessor belonging to the basal population from which H. sapiens, Homo neanderthalensis, and Denisovans emerged. Future findings and additional research may help to elucidate the precise phylogenetic link among them.
This work was conducted by a team of palaeoanthropologists led by María Martinón-Torres of the Department of Anthropology, University College London.
New permanent teeth from Gran Dolina-TD6 (Sierra de Atapuerca). The bearing of Homo antecessor on the evolutionary scenario of Early and Middle Pleistocene Europe
María Martinón-Torres, José María Bermúdez de Castro, Marina Martínez de Pinillos, Mario Modesto-Mata, Song Xing, Laura Martín-Francés, Cecilia García-Campos, Xiujie Wu, Wu Liu
DOI: 10.1016/j.jhevol.2018.12.001
 Close
Close

