Why is the Earth a sphere?
The earth is a sphere because of gravity.

13 September 2022
Around 15 billion years ago the universe formed after the “Big Bang” and continued to expand. Material collided and coalesced under gravitational attraction and about 4.5 billion years ago the Earth was formed. During formation, all the heavy stuff (like iron) sunk to the centre of the planet forming our core and the relatively light stuff (silicate rocks) formed the layer above – the mantle. The outermost layer, the crust, is by far the most chemically complex and is the bit we stand on. Gravity holds the planet together and, if the Earth were made of one homogenous material, it would be a perfect sphere, flattened slightly by its rotation. However, because the Earth is not homogeneus but instead has regions deep below our feet which vary in how dense they are, the Earth is not a perfect sphere and is, instead, slightly wonky-looking – see below! But these images are highly exaggerated, so, as viewed from space, the Earth looks, indeed, very spherical.
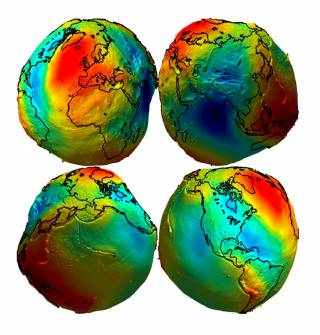
The true shape of the Earth as a consequence of gravity, highly exaggerated by about 10,000 times. The highs and lows represent about 0.2 km difference in height, which is almost nothing compared to the diameter of this sphere which is just under 13,000 km.
So why does the Earth look like a potato? Well the shape defines an equipotential surface – this means that you could put a ball anywhere on this surface and it wouldn’t roll away, despite the highs and lows of the physical Earth. And that is because of changes in density of the material beneath the surface mentioned earlier, which affects the Earth gravity field.
 Close
Close


