New Paper in Energy & Environmental Science
17 April 2018
We are pleased to announce a new paper entitled "
 rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/ee/c7ee02981k#!divAbstract" target="_blank">Efficient Visible Light-Driven Water Oxidation and Proton Reduction by an Ordered Covalent Triazine-Based Framework" published by our group member Jijia Xie et al. in highly cited journal Energy & Environmental Science. This work founded by the Royal Society-Newton Advanced Fellowship grant (NA170422) and EPSRC (EP/N009533/1 and EP/K021192/1).
rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2018/ee/c7ee02981k#!divAbstract" target="_blank">Efficient Visible Light-Driven Water Oxidation and Proton Reduction by an Ordered Covalent Triazine-Based Framework" published by our group member Jijia Xie et al. in highly cited journal Energy & Environmental Science. This work founded by the Royal Society-Newton Advanced Fellowship grant (NA170422) and EPSRC (EP/N009533/1 and EP/K021192/1).
Abstract
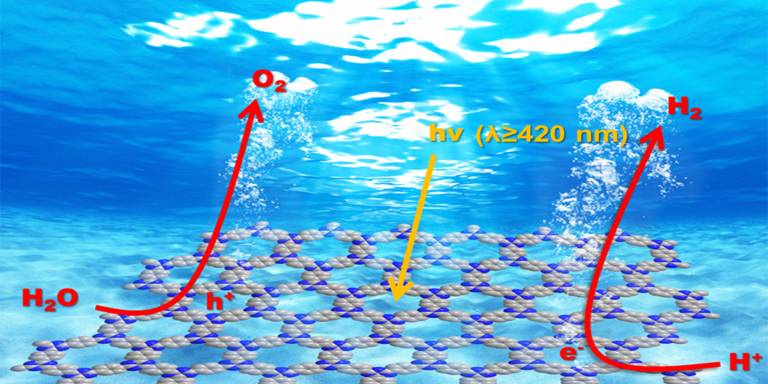
Water oxidation is the rate-determining step in solar driven H2 fuel synthesis and is technically challenging to promote. Despite decades of effort, only a few inorganic catalysts are effective and even fewer under visible light. Recently, attention has been paid to synthetic semiconducting polymers, mainly on graphitic C3N4, with encouraging hydrogen evolution performance but less active for water oxidation. Here, a highly ordered covalent triazine-based framework, CTF-1 (C8N2H4), is synthesised by a very mild microwave-assisted polymerisation approach. It demonstrates extremely high activity for oxygen evolution under visible light irradiation, leading to apparent quantum efficiency (AQE) of nearly 4% at 420 nm. Furthermore, the polymer can also efficiently evolve H2from water. A high AQE of 6% at 420 nm for H2production has also been achieved. The polymer holds great potential for overall water splitting. This exceptional performance is attributed to its well-defined and ordered structure, low carbonisation, and superior band positions.
 Close
Close

