" Molecular Phylogenetics
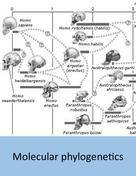 |
Molecular phylogenetics is the science of using DNA and
protein sequences from different species or populations to infer their
evolutionary relationships, which are represented as a phylogeny or tree. The field originated in the 1960s when
protein sequences became available and have gone through explosive growth in
recent years due to accumulation of genomic sequence data. Major methods of phylogeny inference include
parsimony, which infers the tree by minimizing the required number of character
changes, distance-based cluster algorithms, as well as statistical inference
methods such as maximum likelihood and Bayesian. Molecular phylogenetics had a huge impact on studies of human evolution by showing in the 1990s that homo sapiens is closely related to the African apes (chimpanzees and gorillas), and continue to provide important tools for the interpretation of genomic data from the humans and the apes. |
 Close
Close











