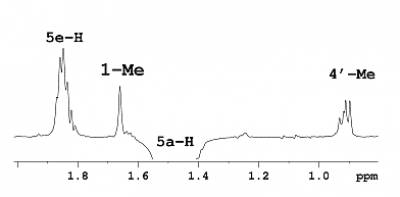
NOE Experiments
NOE experiments are used to quantify nuclear Overhauser effects, which are usually observed between protons that are close in space (i.e., separated by < 5 Å).Typical applications of NOE experiments include determination of stereochemistry of cyclic molecules or measurement of interproton distances. Contrary to sceptical expectations, relatively accurate distance estimates can be obtained using NOEs. For example, in the case of cyclic benzazocinone derivative, interproton distances from NOE measurements showed rms deviations of 0.07-0.08 Å compared to those from quantum-mechanical calculations (see experimental part of J Phys Chem A 2012 116 1093). Note that NOE distance estimates are not restricted to rigid systems alone, but can also be applied in the presence of fast (in the NMR timescale) dynamic processes.
(1) SELNOGPZS is used to record 1D NOESY spectra. A standard practice is to record 2D NOESY spectra on spectrometers operated in automated mode. However, 1D NOESY experiment can in principle provide better sensitivity compared to its 2D analog and can reveal very small NOEs (with signal enhancements of the order of ~0.02%). A previously acquired 1H NMR spectrum will be needed in order to measure the frequency of the signal due to the proton of interest and input the corresponding value in the SELNOGPZS experiment.
Click here for high-resolution version of the above figure.
(2) NOESYZS is used to minimise artifacts in NOESY spectra arising from to the evolution of zero-quantum coherence of J-coupled spins during the mixing time ("ZS" stands for zero-quantum suppression, which is also used in SELNOGPZS). Further details of this experiment and examples of applications can be found in Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2003 42 3938.
(3) EASY-ROESY is recommended for medium-sized molecules (with molecular weights ~1 kDa). The main advantage of this experiment compared to ROESY is that artifacts due to J-couplings and experimental setup conditions are minimised in EASY-ROESY spectra. The method has also been shown to yield reliable intramolecular distances without a sample-specific setup in Chem. Eur. J. 2009 15 585.
 Close
Close