Terminological note
-
Griceans claim that SIs are a type of pragmatic inference called implicature that involves scales, e.g. ⟨or, and⟩, ⟨some, (most,) all⟩, ⟨possible, certain⟩
-
Some neo-Griceans (e.g., Geurts 2010) use the term quantity implicature
- The Gricean derivation of a SI refers to the Maxim of Quantity
- Quantitiy implicatures are a broader concept, subsuming those cases not involving 'scales', e.g., ad hoc implicatures
-
For grammaticalists (e.g., Chierchia, Fox & Spector 2011), SIs are not 'implicatures', but they still use the term 'scalar implicature'
Roadmap
1 Gricean approach
2 Some theoretical issues
2.1 Primary vs. secondary implicatures
2.2 The Symmetry Problem
2.3 Embedded scalar implicatures
3 Grammatical approach
1 Gricean approach
Pragmatic inferences
Not all meaning is encoded in linguisitc expressions
One naturally concludes from (1A) that the speaker does not speak Korean (and more)
But this inference is arguably not part of the meaning of the linguistic expressions used
Gricean implicature
Paul Grice pioneered the study of pragmatic inferences
-
Idea: With the assumption that the speaker is cooperative, one draws inferences based on their (linguistic or non-linguistic) behaviour
-
Grice called such pragmatic inferences implicatures
Cooperativity
It's reasonable to assume that conversational agents are generally cooperative
Pragmatic inferences arise in non-linguistic communication as well
They can be analysed as implicatures too.
Gricean Maxims
What does it mean to be cooperative?
Grice's (tentative) answer: To be a cooperative agent is to follow:
- Maxim of Quantity: Be informative
- Maxim of Quality: Only say what you believe to be true
- Maxim of Relation: Don't say irrelevant things
- Maxim of Manner: Make your utterance orderly
Maxim of Quantity
The Maxim of Quantity is about informativity
- Sub-maxim 1: Don't be underinformative
- Sub-maxim 2: Don't be overinformative
Gricean derivation of SI: Or
- Utterance: "I speak Korean or Japanese"
- Why didn't the speaker say "I speak Korean and Japanese"?
- That would have been more informative
- "I speak K and J" asymmetrically entails "I speak K or J"
- Therefore the Maxim of Quantity favours this alternative
- It must be because asserting the alternative would have been uncooperative
- The Maxims of Relation and Manner would have been respected
- It must have flouted the Maxim of Quality
- Therefore, the speaker doesn't believe the alterantive to be true
Gricean derivation of SI: Some
- Utterance: "Some of the cats are asleep"
- Why didn't the speaker say "All of the cats are asleep"?
- That would have been more informative
- Therefore the Maxim of Quantity favours this alternative
- It must be because asserting the alternative would have been uncooperative
- The Maxims of Relation and Manner would have been respected
- It must have flouted the Maxim of Quality
- Therefore, the speaker doesn't believe the alterantive to be true
Summary
(Neo-)Griceans claim that SIs are implicatures, a type of pragmatic inference generated on the cooperativity assumptions
Recipe for SI:
- Identify a more informative (stronger) alternative (e.g., "and" for "or", "all" for "some")
- Gricean reasoning about Quantity and Quality leads to the negation of the alternative
According to this theory, an SI arises via counterfactual reasoning about a hypothetical utterance of a more informative alternative
Exercise: More SIs
Controversial cases
Bott & Noveck 2004: Experiment 3
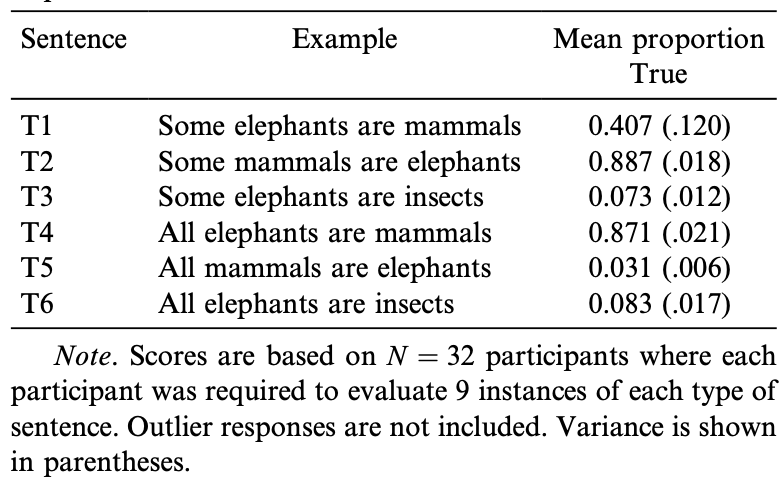
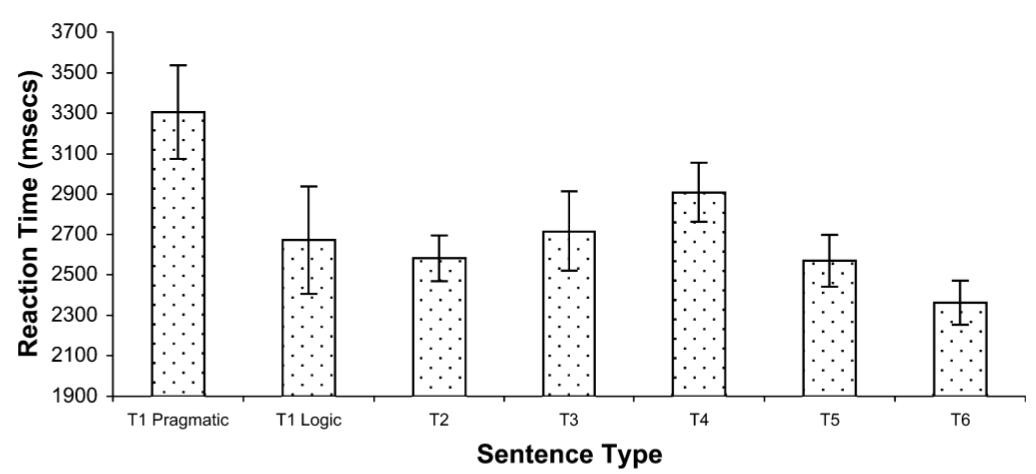
2 Some research topics
2.1 Primary vs. sencodary implicature
According to the Gricean approach:
- Uttering the alternative ψ would have violated the Maxim of Quality
- The Maxim of Quality says: Only utter things you believe to be true, i.e. you have enough evidence for
- So the derived inference is: The speaker does not have enough evidence for the truth of ψ (primary implicature)
But the preceived SI is typically stronger than this: The speaker has enough evidence for the falsity of ψ (secondary implicature)
Epistemic Step
- Primary implicature:
- Secondary implicature:
Neo-Gricean (Spector 2003, Sauerland 2004, etc.) assume that a primary implicature gets strengthened to a secondary implicature via an auxiliary assumption, Opinionatedness (alt. Experthood, Competence)
- Opinionatedness:
1. + 3.
But some experimental evidence that secondary SIs are drawn even if Opinionatedness does not hold (i.e., the speaker is known to be uncertain)
Dieuleveut, Chemla & Spector 2014: Experiment 2
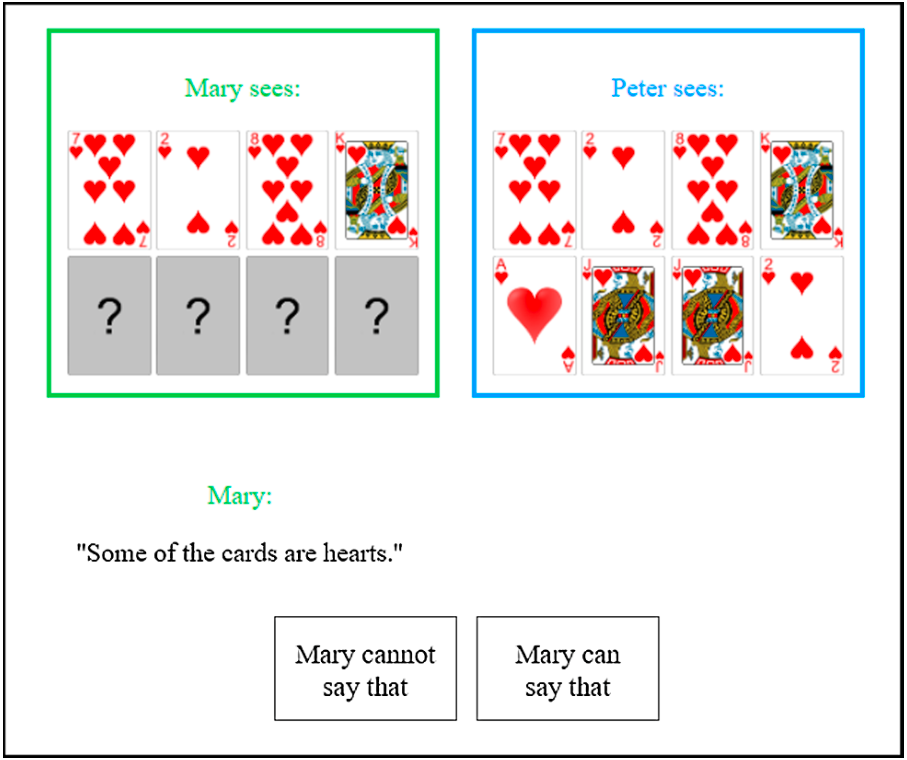

2.2 The Symmetry Problem
Classical Gricean theories are naive about alternatives
The crucial alternative is formed with "all", but one could think of another alternative formed with "some but not all" or "only some"
These alternatives are called symmetric alternatives
Symmetric alternatives cannot be both negated consistently, while maintaining the truth of the prejacent
Structural complexity
One might think that the symmetry between "all" and "some but not all" can be broken by the difference in structural complexity (see Katzir 2007)
But not all symmetry problems can be explained by structural complexity (Romoli 2013, Trinh & Haida 2015, Breheny et al. 2018)
2.3 Embedded SIs
Gricean derivations of SIs only apply at the utterance level
But SIs seem to be able to take scope under logical operators (Chierchia 2004, Chierchia, Fox & Spector 2011, etc.)
Experimental research on SIs
-
Geurts & Pouscoulous 2009 failed to observe evidence for embedded SIs
-
Chemla & Spector 2011 found some evidence
-
More work: Geurts & Van Tiel 2013, Cummins 2014, Van Tiel 2014, Potts, Lassiter, Levy & Frank 2014, Franke, Schlotterbeck & Augurzky 2017, Noveck & Kissine 2018
Difficulties
- By assumption SIs don't arise under 'negative operators'
- With a positive operator over a scalar expression, the local SI reading would asymmetrically entail the global SI reading; crucial data comes from rejections
Non-monotonic contexts
-
E.g., the global reading is true and the local reading false, when 3 students flunked some but not all, 1 flunked all
-
Note that these sentences might lack the global reading altogether
NB: The global and local readings amount to the same thing for 'exactly one'
3 Grammatical Approach
Exh
The grammatical approach to SI was developed mainly to deal with embedded SIs
SIs are triggered by a phonologically null operator called 'Exh' (Groenendijk & Stokhof 1984, Chierchia 2004, Van Rooij & Schulz 2004, Chierchia, Fox & Spector 2011)
Disjunctive alternatives
The disjunct-alts are used to derive the ignorance inference (= primary implicatures)
They sometimes give rise to SIs
Innocent exclusion
The disjunctive-alts are stronger (and hence non-weaker) than the prejacent, but negating them independently will contradict the prejacent
Fox 2007 puts forward innocent exclusion: Negate as many alternatives as possible, while maintaining consistency with the prejacent
E.g.
Remarks
- Exh is similar to only, but not Strawson-DE so does not license weak NPIs
- When Exh appears under an opeartor, the SI takes scope below the operator
- Exh is anti-licensed under negation. There might be other distributional constraints (Fox & Spector 2018)
- The grammatical approach is compatible with Gricean Pragmatics, including certain pragmatic inferences (e.g., ignorance implicatures as primary implicatures)
- The burden of proof is on the grammaticalist
- Embedded SIs (Chierchia 2004, Chierchia, Fox & Spector 2011)
- Obligatory SIs (Chierchia 2004, 2013, etc.)
- Multiple SIs (Franke & Bergen 2020)
Summary
-
In most theories of SI, generation of a scalar implicature involves:
- Reference to an alternative
- Negate the alternative
-
Theories mostly differ with respect to the negation mechanism
- Gricean: Reasoning about Quantity and Quality
- Grammatical: Exh
-
Two experimental topics
A) Implicature priming
B) Scalar diversity