Search for new antibiotics advanced by discovery of key processes within bacterial protein
12 April 2013
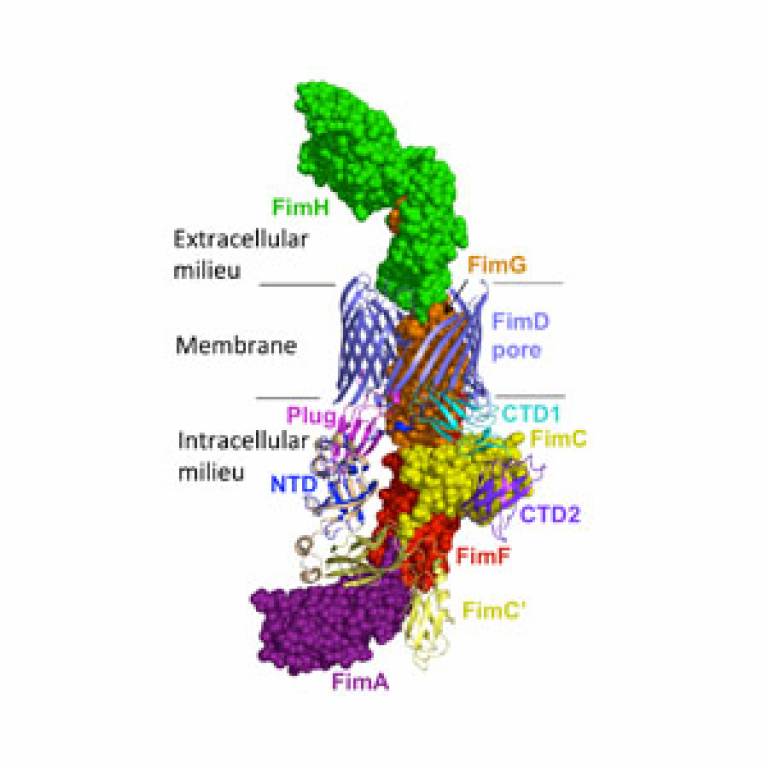
Scientists have discovered how bacteria transport the tiny hair-like strands, called pili, which cover their outer surface from the inside of the cell, where they are assembled, to the exterior.
 Pili are a key target for a new generation
of antibiotics, as without them the bacteria are unable to group together and
to stick to human cells causing infection.
Pili are a key target for a new generation
of antibiotics, as without them the bacteria are unable to group together and
to stick to human cells causing infection.
Published today in Nature, the scientists from the Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology (a joint institute between University College London (UCL) and Birkbeck, University of London) have revealed the structural and energetic process by which the bacteria transport the pili across their outer membrane.
In the cystitis bacteria, pili enable bacteria to group together and then to attach to the wall of the bladder. The bladder cells then engulf the bacteria and this makes antibiotic treatment very difficult. Once inside the bladder cells the bacteria can lie dormant, making recurrent infections common. Scientists believe that a new generation of antibiotics could be developed to disrupt the process of pili biogenesis, making the condition easier to treat.
In 2011, the scientists from the Institute of Structural and Molecular Biology uncovered how pili biogenesis is initiated by the protein FimD - an usher in the outer cell wall. FimD is responsible for recruiting subunits, assembling them into a pilus, and secreting the pilus as it is being formed. From this work, the team was able to develop a model for the way the usher carry out all these tasks. The latest research, funded by the Medical Research Council, provides experimental proofs for the model proposed before and shows how, once the subunits have been assembled, the new pilus is secreted from inside the FimD protein to the exterior, via a pore, across the outer bacterial membrane.
We have been working for a number of years to try and understand the process of pili biogenesis and an understanding of this process takes us a step closer to the development of new antibiotics.
Professor Gabriel Waksman
The team has now revealed that as the pilus is assembled, the first subunit (FimH) engages with the usher and undergoes structural changes. This creates the necessary energy for this subunit, which forms the tip of the pilus, to displace the plug which is normally found inside the pore, and to pass through the pore itself. As subsequent subunits of the pilus pass into the pore, other structural changes in FimH prevent the pilus retreating back through the pore.
The scientists were also able to reveal that within the usher's pore there are specific binding sites for the tip and the subsequent subunits of the pilus. These binding sites are 180 degrees apart within the barrel of the pore (facing each other); so that the pilus is held in a central position as it emerges from the pore, facilitating its exit. Furthermore, they showed that as the pilus passes through the pore it follows a rotational and translational path, enabling subsequent subunits to continue being added within the usher as the tip emerges, while the pilus is still held in a central position.
Professor Gabriel Waksman, at the ISMB, said: "For the first time we have been able to see the structural and energy pathways via which the FimD usher protein facilitates the transport of the newly assembled pilus across the outer membrane of the bacteria. This process is a key target for the development of new antibiotics, as if biogenesis of new pili can be disrupted the bacteria will be unable to attach themselves to human cells and infection will be much less likely.
"We have been working for a number of years to try and understand the process of pili biogenesis and an understanding of this process takes us a step closer to the development of new antibiotics which will successfully treat cystitis - a common and extremely painful condition, as well as other bacterial infections."
Media queries: Bryony Merritt
Links
Research Paper in Nature (£)
The Institute of
Structural and Molecular Biology (ISMB)
Professor Gabriel Waksman
Birkbeck
Medical Research Council
 Close
Close

