New collaborative publication in mBio for the Saiardi Lab
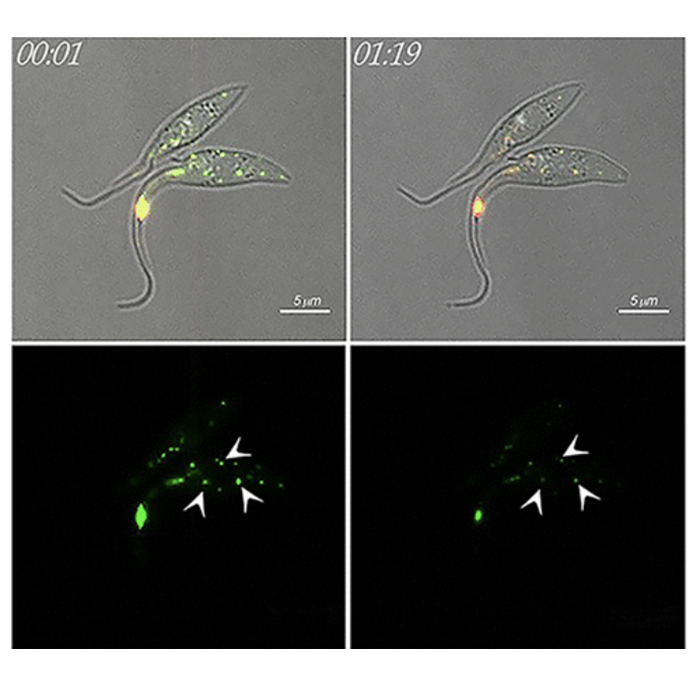
A new publication in mBio for the Saiardi Lab, in collaboration with Brian Mantilla (Durham University) and Roberto Docampo (University of Georgia), identified a novel polyP binding protein in the Histidine Ammonia Lyase (HAL) of Trypanosoma cruzi (the aetiological agent of Chagas disease). The localization of HAL in the polyP-rich acidocalcisome determines its alkalinization, linking this important physiological process to amino acid metabolism.
Article abstract:
Trypanosoma cruzi, the agent of Chagas disease, accumulates polyphosphate (polyP) and Ca2+ inside acidocalcisomes. The alkalinization of this organelle stimulates polyP hydrolysis and Ca2+ release. Here, we report that histidine ammonia lyase (HAL), an enzyme that catalyzes histidine deamination with production of ammonia (NH3) and urocanate, is responsible for acidocalcisome alkalinization. Histidine addition to live parasites expressing HAL fused to the pH-sensitive emission biosensor green fluorescent protein (GFP) variant pHluorin induced alkalinization of acidocalcisomes. PolyP decreased HAL activity of epimastigote lysates or the recombinant protein but did not cause its polyphosphorylation, as determined by the lack of HAL electrophoretic shift on NuPAGE gels using both in vitro and in vivo conditions. We demonstrate that HAL binds strongly to polyP and localizes to the acidocalcisomes and cytosol of the parasite. Four lysine residues localized in the HAL C-terminal region are instrumental for its polyP binding, its inhibition by polyP, its function inside acidocalcisomes, and parasite survival under starvation conditions. Expression of HAL in yeast deficient in polyP degradation decreased cell fitness. This effect was enhanced by histidine and decreased when the lysine-rich C-terminal region was deleted. In conclusion, this study highlights a mechanism for stimulation of acidocalcisome alkalinization linked to amino acid metabolism.
 Close
Close