|
| Kangaroo Care >> Home |
|
|
Kangaroo Care in practiceas presented by WHO Guidelines (2003)
Components
The Kangaroo Care (KC) is characterized by
three major components: Kangaroo Care positionKangaroo Care position is based on direct
skin-to-skin contact between the mother and the new-born baby.
The baby is placed in vertical position between the motherís
breasts. The baby is dressed with nappy, cap and socks to prevent
thermal dispersion. In developing
countries KC policy is to provide 24 hours skin-to-skin contact
with the baby. In developed
countries KC is offered beside incubator care and it is recommended
for at least two hours a day. Ideally, mothers are
employed as incubators and as the main source of nutrition and
stimulation for the baby. Any
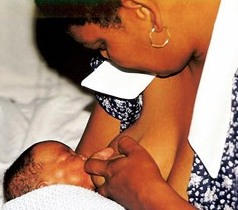
other person can share the role of KC provider. The KC is provided until the baby does not tolerate it any longer. Kangaroo Care feeding
Motherís milk is the best
nutrition for premature and low-birth weight babies and
breastfeeding is the best method of feeding. It should be a
nutritional priority due to the biological uniqueness of preterm
milk, which responds to the infantís gestational age and needs (Morley,
Cole, Powell, Lucas, 1988). KC facilitates the initiation and
establishment of breastfeeding, however feeding a preterm baby is a
very difficult task. Very often they need alternative feeding
methods.
|
|