What is the EU MDR
- The European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) is a set of regulations that governs the production and distribution of medical devices in Europe and Ireland.
- Compliance with the regulation is mandatory for medical device companies that want to sell their products in the European marketplace.
EU MDR Structure
The MDR is split into the following sections:
- Preface: 101 statements on the purpose of the legislation- (pages 1-13)
- Chapters: 10 Chapters- these go into regulatory provisions (pages 13-92)
- Annexes: 15 Annexes- these detail and clarify requirements and provisions (pages 93-175)
- Chapters
Chapter Article Description Chapter I 1 - 4 Scope and definitions Chapter II 5 - 24 Making available on the market Chapter III 25 - 34 Identification and traceability of devices Chapter IV 35 - 46 Notified bodies Chapter V 51 - 60 Classification and conformity assessment Chapter VI 61 - 82 Clinical evaluation and clinical performance Chapter VII 83 - 95 Post market surveillance, vigilance and market suveillance Chapter VIII 96 - 108 Cooperation between members and bodies Chapter IX 109 - 113 Confidentiality and data protection Chapter X 114 - 123 Final provisions - Annexes
Annex Description Annex I General safety and performance requirements - SPR Annex II Technical documentation Annex III Technical documentation on post market surveillance -PMS Annex IV EU Declaration of Conformity - DoC Annex V CE Marking of Conformity - CE Annex VI Information to be Submitted - UDI+ Annex VII Requirements to be met by Notified Bodies Annex VIII Classification Rules Annex IX Conformity Assessment - QMS and Tech Docs Annex X Conformity Assessment - Type Examination Annex XI Conformity Assessment - Production Quality Assurance Annex XII Certficates to be issued by a notified body Annex XIII Procedures for Custom Made Devices Annex XIV Clinical evaluation and post-market clinical follow-up Annex XV Clinical investigations Annex XVI Devices without an intended medical purpose Annex XVII Correlation table
CE Marking - 10 steps to success
1. Determine intended purpose
2. Determine classification
3. Determine conformity assessment routes
4. Comply with conformity requirements
- Quality management system
- Technical documentation
5. Appoint a person responsible for regulatory compliance
6. Undertake assessment by a Notified Body
7. Prepare and sign the Declaration of Conformity
8. Obtain QMS and CE certificate
9. Place CE marking on device
10. YOU’RE DONE-Undertake Post Market Surveillance and ongoing assessments
1. Determining the intended purpose
Is you idea/research actually a medical device?
You can find this out by using the definition provided in Article 2 of the MDR:
Instrument, apparatus, appliance, software, implant, reagent, material or other article intended by the manufacturer to be used, alone or in combination, for human beings for one or more of the following specific medical purposes:
- diagnosis, prevention, monitoring, prediction, prognosis, treatment or alleviation of disease,
- diagnosis, monitoring, treatment, alleviation of, or compensation for, an injury or disability,
- investigation, replacement or modification of the anatomy or of a physiological or pathological process or state,
- providing information by means of in vitro examination of specimens derived from the human body, including organ, blood and tissue donations, which does not achieve its principal intended action by pharmacological, immunological or metabolic means.
The following products shall also be deemed to be medical devices:
- devices for the control or support of conception;
- products specifically intended for the cleaning, disinfection or sterilization of devices
- accessories for medical devices, and products listed in Annex XVI.
2. Determine classification
Devices can be classified into the following categories:
- Class I - generally regarded as low risk
- Class IIa - generally regarded as medium risk
- Class IIb - generally regarded as medium/high risk
- Class III - generally regarded as high risk
Class I devices can be further split into three 'subclasses':
- Is - sterile device
- Im - device with a measuring function
- Ir - is a re-usable device (i.e. surgical equipment)
- Classification examples
Rule Grouping Example 1-4 Non Invasive Devices Blood bags, liquid nitrogen preservation of cells and tissues of human origin, bandages 5-8 Invasive Devices Spinal disc replacement, joint replacement, surgical meshes, stents, breast implants, examination gloves, lancets, neeldes sutures 9-13 Active Devices Software, drill, hearing aid, muscle stimulators, surgical lasers, electrocardiographs, sensors, pumps 14-22 Special Rules Antibiotic bone cements, heparin coated catheters, condoms, IUDs, biological heart valves, drug eluting stents, X-Ray Films
3. Determine conformity assessment routes
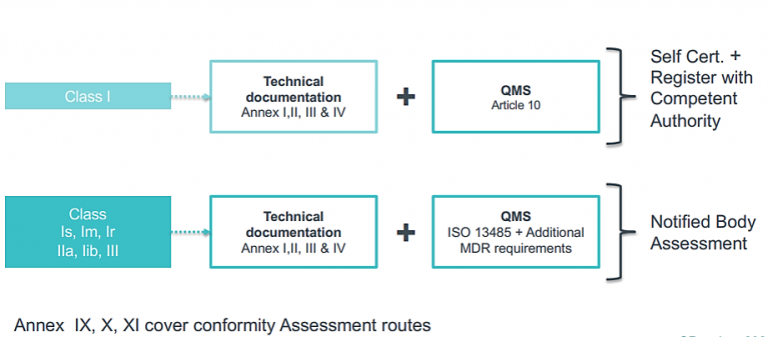
4. Comply with conformity requirements
Quality Management Systems (QMS)
- Class I devices - Only need to comply with Article 10 of the MDR for QMS requirements
- Class Is, Im, Ir, IIa, Iib, III - We MUST have a quality management system in place, many companies comply to this standard- ISO 13485:2016- Medical devices-Quality management systems-Requirements for Regulatory purposes.
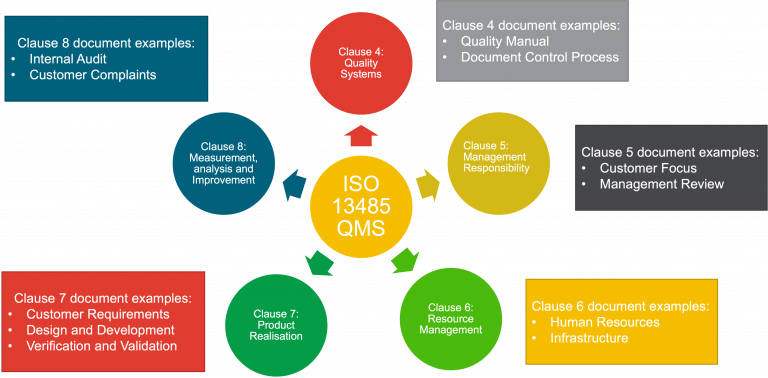
The QMS covers the structure, responsibilities, procedures, processes and management resources required to achieve compliance with the provisions of the MDR. It is basically a big manual of how to do things and a set of procedures and processes to make sure our devices are manufactured in a consistent way.
An ISO 13485 QMS is usually structured like the diagram below:
Technical Documents
All classification of devices require technical documents. The following Annexes in the MDR relate to technical file development:
- Annex I General Safety and Performance Requirements (SPR)
- Annex II Technical Documentation
- Annex III Technical Documentation on Post Market Surveillance
- Annex IV Declaration of Conformity
Example technical documents:
1. Device description and specification:
- Intended purpose of the device, how it works, product specification, materials, components, classification.
2. Information supplied by the manufacturer:
- Labels, promotional material, language requirements.
3. Design and manufacturing information:
- Design stages, manufacturing process, critical ingredients and suppliers, product release process, address of manufacturing sites and certificates.
4. Safety and risk management:
- Summary of risks identified, risk management plan
5. Device verification and validation:
- Summary of the results of verification and validation activities e.g. pre clinical and clinical data, clinical evaluation report, engineering tests, biocompatibility data, sterilization, electrical safety and electromagnetic compatibility, software verification and validation, post market clinical follow up plan, post market surveillance plan etc.
You may have to adhere to a range of other standard to demonstrate conformity
| Area | Standard |
|---|---|
| Risk management | EN ISO 14971 |
| Usability / Human factor | EN 62366 |
| Biocompatibility | EN ISO 10933 -1 to 20 |
| Clinical investigation | EN ISO 14155 |
| Software | EN 62304 + MEDDEV 2. 1/6 (guidance) + MDCG |
| Information security | ISO 27001 |
| Medical Electrical Equipment | EN 60601 series |
| Symbols | EN ISO 15223 |
5. Appoint a person responsible for regulatory compliance (PRRC-Article 15)
The appointment of person(s) responsible for regulatory compliance (PRRC) is required. They must be suitable for the role and have expertise in the field of medical devices.
A PRRC will be responsible for carrying out/ensuring:
- Conformity of devices before release
- Technical documentation are up to date and the Declaration of Conformity
- Compliance with post market surveillance and vigilance requirements
6. Undertake assessment by a Notified Body
Notified bodies provide conformity assessment services. Conformity assessments usually take the form of external audit that is split into two stages.
- Examples of Notified Bodies
Body type Name Country NB 0086 BSI Assurance UK Ltd United Kingdom NB 2797 BSI Group The Netherlands B.V. Netherlands NB 2409 CE Certiso Orvos - és Kórháztechnikai Ellenőrző és Tanúsító Kft Hungary NB 1912 DARE!! Services B.V. Netherlands NB 0344 DEKRA Certification B.V. Netherlands NB 0124 DEKRA Certification GmbH Germany NB 2460 DNV GL Presafe AS Norway NB 0051 IMQ ISTITUTO ITALIANO DEL MARCHIO DI QUALITÀ S.P.A. Italy NB 0482 MEDCERT ZERTIFIZIERUNGS- UND PRÜFUNGSGESELLSCHAFT FÜR DIE MEDIZIN GMBH Germany NB 0050 National Standards Authority of Ireland (NSAI) Ireland NB 0197 TÜV Rheinland LGA Products GmbH Germany NB 0123 TÜV SÜD Product Service GmbH Zertifizierstellen Germany
7. Prepare and sign the Declaration of Conformity (DoC) - Annex IV
With the declaration of conformity, the manufacturer certifies that the MDR’s general safety and performance requirements have been met by the respective medical device. Without a valid declaration of conformity, a medical device cannot be placed on the market.
It includes information such as:
- Product and trade name
- Risk class
- Single Registration Number

8 & 9 Obtain QMS and CE Certificate, and place CE marking on device
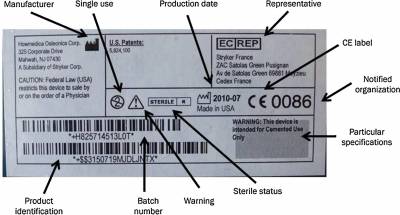
Image from Materials vigilance and traceability

10. YOU'RE DONE - Undertake Post Market Surveillance and ongoing assessments
Post Market Surveillance (PMS) - Annex III
You need to continue to maintain regulatory compliance.
PMS is a systematic procedure to:
- Collect and review experience gained from devices placed on the market and to identifying any necessary corrective or preventive actions – Article 2.
- Actively and systematic gather, record and analyse relevant data on quality, performance and safety of a device throughout its entire lifetime.
- This surveillance should be based on your post-market surveillance plan, the requirements for which are set out in Section 1 of Annex III.
The post-market surveillance plan shall be part of the technical documentation specified in Annex II – Article 84 MDR.
 Close
Close

