ICGNMD: Our Approach to Genomics
The ICGNMD recognises the importance of combining in-depth phenotyping, specialised clinical expertise, and bioinformatic knowledge to achieve the best possible diagnostic rates for our participants.
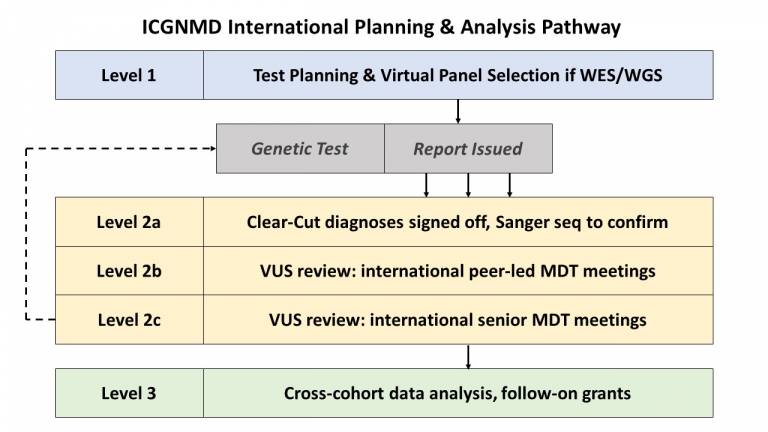
- Level 1 – Test Planning
Clinical cases are discussed by international fellows and their UK collaborators and a testing strategy is developed.
This may involve single gene tests such as MLPA or repeat primed PCR, or broader investigations (e.g. whole exome sequencing).
Much focus is paid to the content of virtual gene panels applied to such data, and a clear plan for the bioinformatic processing of data is agreed. Where exome data exists, e.g., from a private provider, ICGNMD fellows may submit this for re-analysis via our bespoke pipeline.
- Level 2 - Interpretation
Content placeholder
Data is interpreted and discussed by the relevant international fellow and their UK collaborators.
Level 2a
‘Clear cut diagnoses’ are signed off by senior researchers, and may progress to Sanger sequencing for confirmation.
Level 2b
Variants of uncertain significance are brought to a peer-led fellows meeting where a group of clinical fellows and bioinformaticians interpret challenging variants, consider whether variants are worth pursuing, and suggest next steps for confirmation e.g., segregation, and reverse phenotyping.
Level 2c
Very challenging cases can be brought to a principle investigator meeting for further consideration from international experts. We are now establishing dedicated meetings for specific disease groups including inherited neuropathies, mitochondrial disease, congenital muscular dystrophies and myopathies, complex neurogenetic conditions, and FSHD.
Further research
Data is available for interrogation for novel genetic causes of disease. In some cases samples are referred for whole genome sequencing. Our future grants aim to expand our functional genomic capabilities.
 Close
Close


