Summary
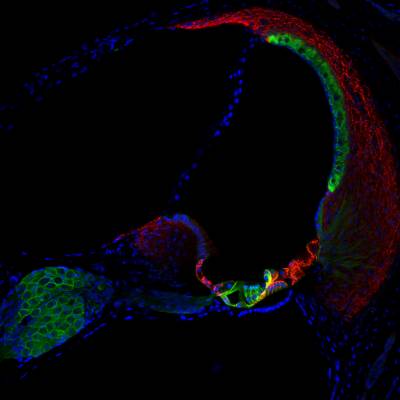
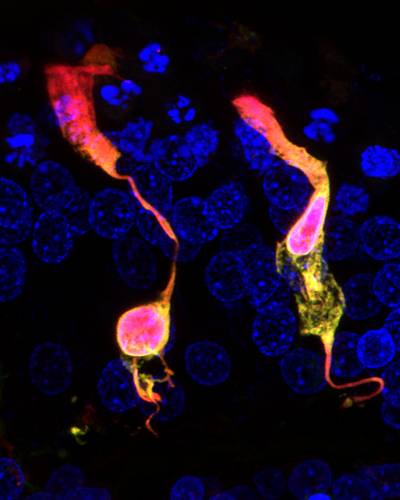
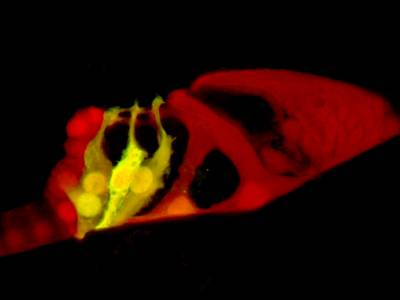
Normal hearing relies on the maintenance of a constant chemical environment within the tissues of the inner ear. This so-called “homeostasis” protects the sensory hair cells from damage, ensuring the exquisite sensitivity and frequency selectivity of our hearing. Inner ear homeostasis is carried out by numerous cellular mechanisms, often which are reliant on each other. Failure of any of these processes can result in hair cell death, and permanent hearing loss. It is our aim to gain a better understanding of these mechanisms, and to learn how we can translate these findings into clinical treatments to prevent hearing loss
We work closely with Andy Forge’s lab to decipher the regulation of homeostasis in the cochlea and vestibular organs, including changes occurring during ageing and regeneration. In particular, we study the function of connexins (gap junction channel subunits) in supporting cells, and how they work to protect hair cells from damage.
Relevant Publications
- See our full publication list
- Kelly, J.J., Shao Q., Jagger, D.J., Laird, D.W. Cx30 exhibits unique characteristics including a long half-life when assembled into gap junctions. Journal of Cell Science 128, 3947-3960, 2015.
- Taylor RR, Jagger DJ, Saeed SR, Axon P, Donnelly N, Tysome N, Moffatt D, Irving R, Monksfield P, Coulson C, Freeman SR, Lloyd SK, Forge A. Characterising human vestibular sensory epithelia for experimental studies: new hair bundles on old tissue and implications for therapeutic interventions in ageing. Neurobiology of Ageing 36, 2068-2084, 2015.
- Jagger DJ, Nickel R, Forge A. Gap Junctional Coupling is Essential for Epithelial Repair in the Avian Cochlea. Journal of Neuroscience 34, 15851-15860, 2014.
- Chen J, Ingham N, Kelly J, Jadeja S, Goulding D, Pass J, Mahajan VB, Tsang SH, Nijnik A, Jackson IJ, White JK, Forge A, Jagger DJ, Steel KP. Spinster homolog 2 (Spns2) deficiency causes early onset progressive hearing loss. PLoS Genetics 10, e1004688, 2014.
- Forge A. Jagger DJ. Kelly JJ. Taylor RR. Connexin30 mediated intercellular communication plays an essential role in epithelial repair in the cochlea. Journal of Cell Science 126, 1703-1712, 2013.
 Close
Close