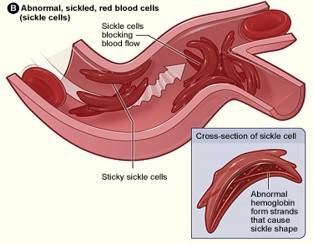
Globally, there is also a pressing need to explore ways to reduce the risk of serious complications such as painful crises, lung disease, and sleep disordered breathing. SCD is the most common cause of childhood stroke; in addition, up to 30% children have ‘silent’ cerebral infarction (SCI) detectable using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
SCD is also associated with progressive cognitive difficulties from infancy, even in school-age children with no apparent SCI. Adults and children with SCA have long-term healthcare needs, which affect quality of life and require attention from healthcare professionals.
 Close
Close