Physiological functions of the clathrin light chains
The canonical form of clathrin is composed of CHC17 and clathrin light chains (CLCs). CLCs bind in a 1:1 stoichiometric ratio with CHC17 and are known to be required for the endocytosis of some (but not all) cargo to modulate the biophysical properties of clathrin (such as the ability of clathrin to deform membranes) and to mediate protein-protein interactions. However, the full scope of CLC functions remain to be defined. In particular, CLCs are encoded by two genes, which give rise to CLCa and CLCb, and tissue specific splice variants of these genes, resulting in a total of six CLC isoforms. CLCa and CLCb share about 60% identity, and each isoform and their tissue-specific distribution are conserved throughout mammalian species, suggesting that the CLC isoforms perform non-redundant, tissue specific roles. We are interested in understanding how diversity amongst the CLCs allows clathrin function to be fine-tuned to meet tissue-specific physiological needs.
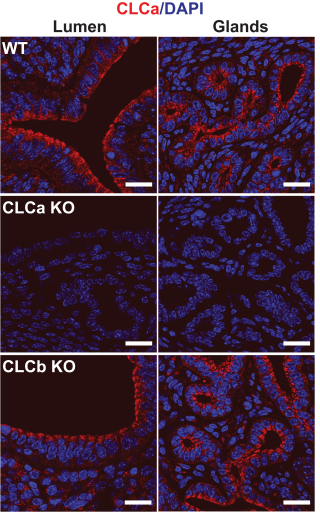
Clathrin light chains CLCa and CLCb have non-redundant roles in epithelial lumen formation.
Chen, Briant, et al. Life Sci Alliance - 2023
- Constitutive CLCa or CLCb knockout mice were characterised. 50% of CLCa KO pups die within 3 days of birth. Most surviving CLCa KO mice and all CLCb mice have mild phenotypes.
- CLCa KO mice are unable to breed with CLCa KO mice
- >40% of female mice over 4 months of age develop pyometra (infected uterus) and have defective gland development. Luminal epithelia aberrantly express FOXA2 and K14, indicating a change in epithelial subtype.
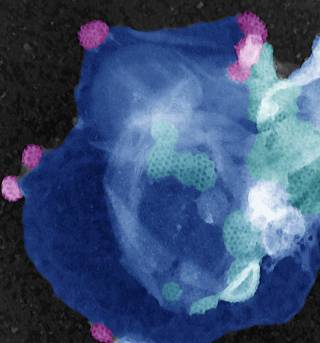
- Endometria (Ishikawa) and colon (Caco-2) derived cell culture lines showed loss of CLCa or CLCb prevented normal apico-basal polarity formation in vitro in 3D cysts.
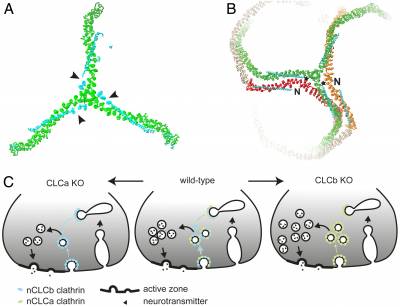
Clathrin light chain diversity regulates membrane deformation in vitro and synaptic vesicle formation in vivo.
Redlingshöfer, McLeod, Chen, et al. PNAS - 2020
- Neuronal CLC splice inserts influence assembly properties.
- Clathrin assemblies containing a mixture of neuronal (n) CLCa and nCLCb are more efficient at deforming membranes in vitro than clathrin assemblies containing only nCLCa or nCLCb.
- Correspondingly, mice require both nCLCa and nCLCb for synaptic function in vivo.
- Mice lacking nCLCa have reduced synaptic vesicles and neurotransmission, while mice lacking nCLCb have increased synaptic vesicles and activity.
Clathrin light chains' role in selective endocytosis influences antibody isotope switching
Wu, Majeed, et al. PNAS - 2016
- Brain, liver and heart tissues in mice express equal levels of CLCa and CLCb, whereas lymphoid tissues express predominantly CLCa.
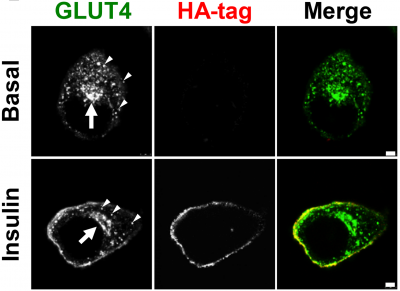
- Internalisation of TGFβ receptor R2 (TGFβR2) in B cells is CLC-dependent.
- Increased TGFβR2 signalling in CLCa knockout B cells increases IgA-expressing B cells.
- CLCs are required for uptake of some G-protein-coupled receptors (CXCR4, DOR) but dispensable for others (CXCR5, β2-adrenergic receptor).

 Close
Close